Lab 7:Create dynamic tooling based agents
Building a ReWoO agent using tools which get selected at run time
Overview
In this lab we are going to create an Agent that will have access to tools to find weather. You will be able to ask this agent questions, watch it call the required tools, and have conversations with it. However the agent is able to select dynamically the tools it needs to invoke. We will use RAG to get the list of tools needed based on the user input. The lab will cover the following scenario:
What gets covered in this lab:
we will cover these aspects below: - Create a dynamic tool selector - Agent configuration and create Graph - Create with multiple tools - Cover rewoo agents in detail - Add RAG to create the tools on the fly
Use case details
The agent is a weather assistant and will need a coupel of functions to create the weather report for the place and day
- Initial User Input:
-
User will send in a place
-
Provide additional details about suggested location:
-
Use weather tool to look up the location
-
ask the app to run the functions:
- Showcase tool execution based on human approval
Architecture [ Weather lookup]
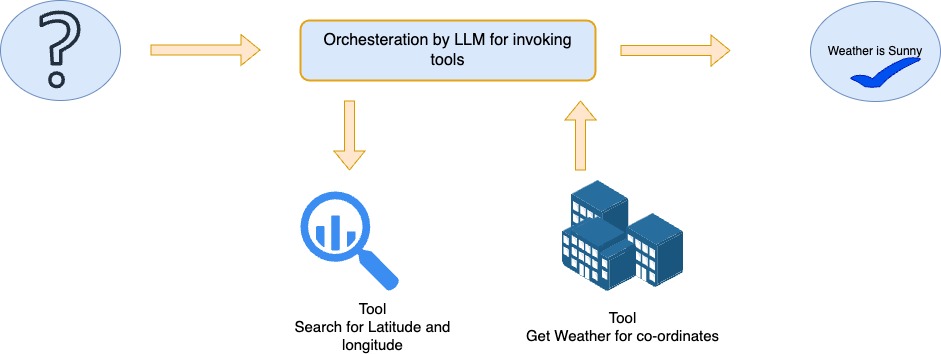
Setup
Let's start with installing required packages.
# %pip install -U --no-cache-dir \
# "langchain==0.3.7" \
# "langchain-aws==0.2.6" \
# "langchain-community==0.3.5" \
# "langchain-text-splitters==0.3.2" \
# "langchainhub==0.1.20" \
# "langgraph==0.2.45" \
# "langgraph-checkpoint==2.0.2" \
# "langgraph-sdk==0.1.35" \
# "langsmith==0.1.140" \
# "pypdf==3.8,<4" \
# "ipywidgets>=7,<8" \
# "matplotlib==3.9.0" \
# "faiss-cpu==1.8.0" \
# "pandas==2.2.3"
Agents
An AI agent is a software program or system that uses artificial intelligence techniques to perceive its environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals. These agents are designed to operate with some degree of autonomy and can adapt their behavior based on their experiences and the information they receive. Their capabilities extend beyond simple interactions, enabling them to engage in complex decision-making, problem-solving, and task execution with or without human intervention
Key characteristics of AI agents include:
Perception: The ability to gather information from their environment through sensors or data inputs. Decision-making: Using AI algorithms to process information and determine the best course of action. Action: The capability to execute decisions and interact with the environment or users. Learning: The ability to improve performance over time through experience and feedback. Autonomy: Operating independently to some degree, without constant human intervention. Goal-oriented: Working towards specific objectives or tasks.
LLM's are great with Classification problems and this has enabled Agents to be a reality
We create a Bedrock client that is used to configure LLM in LangChain to use Bedrock.
from langchain_aws import ChatBedrock
import boto3
# ---- ⚠️ Update region for your AWS setup ⚠️ ----
bedrock_client = boto3.client("bedrock-runtime", region_name="us-west-2")
Language Model
The LLM powering all of our agent implementations in this lab will be Claude 3 Sonnet via Amazon Bedrock. For easy access to the model we are going to use ChatBedrockConverse class of LangChain, which is a wrapper around Bedrock's Converse API.
from langchain_aws import ChatBedrockConverse
llm = ChatBedrockConverse(
model = "anthropic.claude-3-haiku-20240307-v1:0",
temperature=0,
max_tokens=None,
client=bedrock_client,
# other params...
)
Build the weather tool system
Tools
Let's create tools that will be used by our agents to find the latitude and longitude of the place and then use that to find the weather
Tools are external resources, services, or APIs that an LLM agent can access and utilize to expand its capabilities and perform specific tasks. These supplementary components allow the agent to go beyond its core language processing abilities, enabling it to interact with external systems, retrieve information, or execute actions that would otherwise be outside its scope. By integrating tools, LLM agents can provide more comprehensive and practical solutions to user queries and commands.
A tool consists of:
- The name of the tool.
- A description of what the tool does.
- A JSON schema defining the inputs to the tool.
- A function (and, optionally, an async variant of the function)
in LangGraph Tools can be specified by decorating them with the @tool decorator. This parses the respective function name as well as docstrings and input parameters into a name, description and interface definition. When a tool is bound to a model, this information is provided as context to the model. Given a list of tools and a set of instructions, a model can figure out how to call one or more tools with specific inputs as well as when to call which tool.
We will create a tool that uses historic travel information of different users to find a vacation destination based on user' profile and travel history of similar users. The tool will use the local csv file to retrieve historical data about travel destinations. It will then analyze the data and return the most popular destination for the user.
APIs
we have 3 API's which we will use - First will be to pass in the place and get the latitude and longitude - Second to get the weather based on the co-ordinates - Third will be a RAG system to return the toosl which need to be called at run-time via semantic searches leveraging vector store.
we will find the tools which the user can travel and then use that to find other similiar destinations using the vector store
Helper function to pretty print
from io import StringIO
import sys
import textwrap
from langchain.llms.bedrock import Bedrock
from typing import Optional, List, Any
from langchain.callbacks.manager import CallbackManagerForLLMRun
def print_ww(*args, width: int = 100, **kwargs):
"""Like print(), but wraps output to `width` characters (default 100)"""
buffer = StringIO()
try:
_stdout = sys.stdout
sys.stdout = buffer
print(*args, **kwargs)
output = buffer.getvalue()
finally:
sys.stdout = _stdout
for line in output.splitlines():
print("\n".join(textwrap.wrap(line, width=width)))
Create the 2 tools for weather lookup
- Find latitude and longitude
- Use these values to pass into the weather and return the weather back
import requests
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_core.runnables.config import RunnableConfig
@tool ("get_lat_long")
def get_lat_long(place: str) -> dict:
"""Returns the latitude and longitude for a given place name as a dict object of python."""
url = "https://nominatim.openstreetmap.org/search"
headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/39.0.2171.95 Safari/537.36'}
params = {'q': place, 'format': 'json', 'limit': 1}
response = requests.get(url, params=params, headers=headers).json()
if response:
lat = response[0]["lat"]
lon = response[0]["lon"]
return {"latitude": lat, "longitude": lon}
else:
return None
@tool ("get_weather")
def get_weather(latitude: str, longitude: str) -> dict:
"""Returns weather data for a given latitude and longitude."""
url = f"https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast?latitude={latitude}&longitude={longitude}¤t_weather=true"
response = requests.get(url)
print_ww(f"get_weather:tool:invoked::response={response}:")
return response.json()
#get_weather_tool = StructuredTool.from_function(get_weather)
tools_list = [get_lat_long,get_weather]
for tools_s in tools_list:
print_ww(f"Tool:name={tools_s.name}::args={tools_s.args}:: discription={tools_s.description}::")
Tool:name=get_lat_long::args={'place': {'title': 'Place', 'type': 'string'}}:: discription=Returns
the latitude and longitude for a given place name as a dict object of python.::
Tool:name=get_weather::args={'latitude': {'title': 'Latitude', 'type': 'string'}, 'longitude':
{'title': 'Longitude', 'type': 'string'}}:: discription=Returns weather data for a given latitude
and longitude.::
In this section, we prepare our retriever:
We will create a simple csv with text and then the tools as a list
the Vector store process can be similiar to the diagram below
from langchain_aws.embeddings.bedrock import BedrockEmbeddings
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.retrievers import ParentDocumentRetriever
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
import csv
# import faiss
from io import BytesIO
import tempfile
from langchain_community.document_loaders.csv_loader import CSVLoader
from uuid import uuid4
import faiss
from langchain_community.docstore.in_memory import InMemoryDocstore
embeddings_model = BedrockEmbeddings(
client=bedrock_client, model_id="amazon.titan-embed-text-v1"
)
child_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
separators=[",", "\n", "\n\n"], chunk_size=2000, chunk_overlap=250
)
tools_string = """
'for place only use this', ['get_lat_long',]\n
'for weather search use this', ['get_lat_long','get_weather']\n
'for all other queries use this', []
""".strip()
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False, mode="w+") as temp_file:
temp_file.write(tools_string)
temp_file_path = temp_file.name
loader = CSVLoader(file_path=temp_file_path, csv_args={"fieldnames": ["search_string", "functions_to_be_called"],} )
data = loader.load()
index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(len(embeddings_model.embed_query("hello world")))
# vector_store = FAISS(
# embedding_function=embeddings_model,
# index=index,
# docstore=InMemoryDocstore(),
# index_to_docstore_id={},
# )
# vector_store.add_documents(documents=data, ids=[str(uuid4()) for _ in range(len(data))])
vector_store = FAISS.from_documents(embedding=embeddings_model, documents=data)
retriever = vector_store.as_retriever(search_type="mmr", search_kwargs={"k": 1})
Check to see if the retiever returns the appropriate tools list back
retriever.invoke("find me the weather for Seattle")
[Document(metadata={'source': '/var/folders/dj/gb0dzz0s7377l6w8dyf1yx_00000gq/T/tmpzf8bjxb9', 'row': 1}, page_content="search_string: 'for weather search use this'\nfunctions_to_be_called: ['get_lat_long'\nNone: 'get_weather']")]
We now create a specialized retrieval tool using the create_retriever_tool function from LangChain:
- The tool is based on our previously set up retriever.
- We name it "search_user_question".
- Its description specifies that it searches through multiple rtools lists specified in the CSV as RAG
- The tool is designed to find information that matches the user's choice needed
- It's instructed to search based only on the keywords mentioned in the user's input.
from langchain.tools.retriever import create_retriever_tool
retriever_tool = create_retriever_tool(
retriever,
"search_user_question",
"Searches through multiple documents. Only search based on the keyword mentioned in user input. and return the document content as is",
)
Now we also add both tools to the list of tools our agent will be able to use.
retriever_tool.invoke("find me the weather for Seattle")
"search_string: 'for weather search use this'\nfunctions_to_be_called: ['get_lat_long'\nNone: 'get_weather']"
Now create a ReACT agents which is using the retriever in this case and returns the list of the functions ot be called
- it will invoke the retriever
- using the string sent by the user look up the functions
- parse the return of the value and then creates the list correctly
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
agent_selector_agent = create_react_agent(llm,tools=[retriever_tool,])
user_message = 'find me the weather for Seattle'
def invoke_retriever(user_message:str):
ret_messages = agent_selector_agent.invoke({"messages": [HumanMessage(f"""
Use the tool attached to get the functions needed for '{user_message}'.
Parse the response to extract just the functions to be called and only return the names of the functions to be called comma separated
""")],})
func_list = ret_messages['messages'][-1].content
print(f"invoke_retriever::result={func_list}::user_message={user_message}::")
func_list = [func_name.strip().replace(" ","").replace("-", "") for func_name in func_list.split(":")]
func_list = func_list[1:] #- returns a list
func_list = func_list[0].split(",")
return func_list, type(func_list)
invoke_retriever(user_message)
invoke_retriever::result=The functions to be called are: get_lat_long, get_weather::user_message=find me the weather for Seattle::
(['get_lat_long', 'get_weather'], list)
Test with another message where we pass in just the location needed so only 1 tool should be invoked
user_message = 'find me the place called Seattle'
final_tuple = invoke_retriever(user_message)
final_tuple
invoke_retriever::result=The functions to be called are: get_lat_long::user_message=find me the place called Seattle::
(['get_lat_long'], list)
Create a Stateful Graph with ReWoO Agent
For any multi-turn and multi-step workflows we have to either create or leverage the ReACT agents or the ReWoO agents. We will create the node for tools which will be dynamically invoked based on the response of the agents.
Let's start with initializing the agent with the LLM and the tools.

Build Dynamic Tool calling Graph
Agents have 2 main constructs - Planners who create a detailed plan for task execution and then Solvers who executes the planned steps and Integrates outputs from executed tasks to formulate a final response. These 2 work hand-in-hand to execute a particular task. This implies:
We will create the following nodes: - Dynamic tool serarch. This invokes the RAG retriever to match the tools which are needed for the invocations - Bind the tools at run time after looking up the tools from the tool catalog - Run the Tool Nodes which is all of the tools from thne catalog - assemble the results and return those back to the user
from typing import Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
from IPython.display import Image, display
# Define the state structure using TypedDict.
# It includes a list of messages (processed by add_messages)
# and a list of selected tool IDs.
class State(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
selected_tools: list[str]
builder = StateGraph(State)
tool_registry = {'retriever_tool':retriever_tool, 'get_lat_long': get_lat_long, 'get_weather':get_weather}
# Retrieve all available tools from the tool registry.
tools = list(tool_registry.values())
# The agent function processes the current state
# by binding selected tools to the LLM.
def dynamic_agent(state: State):
print(f"dynamic_agent::{state['selected_tools']}")
# Map tool IDs to actual tools
# based on the state's selected_tools list.
selected_tools = [tool_registry[id] for id in state["selected_tools"]]
# Bind the selected tools to the LLM for the current interaction.
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(selected_tools)
# Invoke the LLM with the current messages and return the updated message list.
return {"messages": [llm_with_tools.invoke(state["messages"])]}
# The select_tools function selects tools based on the user's last message content.
def select_tools(state: State):
last_user_message = state["messages"][-1]
query = last_user_message.content
final_tuple = invoke_retriever(query) #- returns (['get_lat_long', 'get_weather'], list)
tool_documents = final_tuple[0]
return {"selected_tools": tool_documents} #- [document.id for document in tool_documents]}
builder.add_node("dynamic_agent", dynamic_agent)
builder.add_node("select_tools", select_tools)
tool_node = ToolNode(tools=tools)
builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
builder.add_conditional_edges("dynamic_agent", tools_condition, path_map=["tools", "__end__"])
builder.add_edge("tools", "dynamic_agent")
builder.add_edge("select_tools", "dynamic_agent")
builder.add_edge(START, "select_tools")
graph = builder.compile()
#display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
Test with the find weather
config = {"configurable": {"user_id": 9188}}
graph.invoke({"messages": [HumanMessage(content='find me the weather for Seattle')]},config)
invoke_retriever::result=The functions to be called are: get_lat_long, get_weather::user_message=find me the weather for Seattle::
dynamic_agent::['get_lat_long', 'get_weather']
dynamic_agent::['get_lat_long', 'get_weather']
get_weather:tool:invoked::response=<Response [200]>:
dynamic_agent::['get_lat_long', 'get_weather']
{'messages': [HumanMessage(content='find me the weather for Seattle', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='05abf5bc-ceb5-4798-909c-746e2ee4a389'),
AIMessage(content=[{'type': 'text', 'text': "Okay, let's find the weather for Seattle:"}, {'type': 'tool_use', 'name': 'get_lat_long', 'input': {'place': 'Seattle'}, 'id': 'tooluse_uIheSjNtSa6lVgM-Odcvrw'}], additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={'ResponseMetadata': {'RequestId': 'dbff02a2-27c6-4678-b79e-fc55c0d944f1', 'HTTPStatusCode': 200, 'HTTPHeaders': {'date': 'Thu, 28 Nov 2024 22:53:58 GMT', 'content-type': 'application/json', 'content-length': '333', 'connection': 'keep-alive', 'x-amzn-requestid': 'dbff02a2-27c6-4678-b79e-fc55c0d944f1'}, 'RetryAttempts': 0}, 'stopReason': 'tool_use', 'metrics': {'latencyMs': 945}}, id='run-f2c595ac-eab0-4b01-9cfc-8ca2f0b98fa3-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'get_lat_long', 'args': {'place': 'Seattle'}, 'id': 'tooluse_uIheSjNtSa6lVgM-Odcvrw', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 413, 'output_tokens': 67, 'total_tokens': 480}),
ToolMessage(content='{"latitude": "47.6038321", "longitude": "-122.330062"}', name='get_lat_long', id='db266b42-730d-40b0-9b49-a27b76a61a94', tool_call_id='tooluse_uIheSjNtSa6lVgM-Odcvrw'),
AIMessage(content=[{'type': 'text', 'text': "Now that we have the latitude and longitude for Seattle, let's use that to get the weather data:"}, {'type': 'tool_use', 'name': 'get_weather', 'input': {'latitude': '47.6038321', 'longitude': '-122.330062'}, 'id': 'tooluse_q6VEa7uyT2i1BH2qn34jcw'}], additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={'ResponseMetadata': {'RequestId': '54895319-2552-4fda-8e3c-37aaae93a008', 'HTTPStatusCode': 200, 'HTTPHeaders': {'date': 'Thu, 28 Nov 2024 22:53:59 GMT', 'content-type': 'application/json', 'content-length': '420', 'connection': 'keep-alive', 'x-amzn-requestid': '54895319-2552-4fda-8e3c-37aaae93a008'}, 'RetryAttempts': 0}, 'stopReason': 'tool_use', 'metrics': {'latencyMs': 772}}, id='run-5bb081b8-eae4-4e2e-9ea0-319dfcc83763-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'get_weather', 'args': {'latitude': '47.6038321', 'longitude': '-122.330062'}, 'id': 'tooluse_q6VEa7uyT2i1BH2qn34jcw', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 510, 'output_tokens': 101, 'total_tokens': 611}),
ToolMessage(content='{"latitude": 47.595562, "longitude": -122.32443, "generationtime_ms": 0.07390975952148438, "utc_offset_seconds": 0, "timezone": "GMT", "timezone_abbreviation": "GMT", "elevation": 40.0, "current_weather_units": {"time": "iso8601", "interval": "seconds", "temperature": "°C", "windspeed": "km/h", "winddirection": "°", "is_day": "", "weathercode": "wmo code"}, "current_weather": {"time": "2024-11-28T22:45", "interval": 900, "temperature": 6.0, "windspeed": 5.3, "winddirection": 332, "is_day": 1, "weathercode": 3}}', name='get_weather', id='c5c09104-1314-478e-b3b8-5ccbfd8fcd0f', tool_call_id='tooluse_q6VEa7uyT2i1BH2qn34jcw'),
AIMessage(content='The weather data shows that the current temperature in Seattle is 6°C, with wind speeds of 5.3 km/h from the northwest, and partly cloudy skies.', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={'ResponseMetadata': {'RequestId': '2222424a-88c5-4e6a-a37e-d925b5992c24', 'HTTPStatusCode': 200, 'HTTPHeaders': {'date': 'Thu, 28 Nov 2024 22:54:01 GMT', 'content-type': 'application/json', 'content-length': '328', 'connection': 'keep-alive', 'x-amzn-requestid': '2222424a-88c5-4e6a-a37e-d925b5992c24'}, 'RetryAttempts': 0}, 'stopReason': 'end_turn', 'metrics': {'latencyMs': 508}}, id='run-99ef9f2d-4689-495c-a90c-e00369ae1af2-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 820, 'output_tokens': 43, 'total_tokens': 863})],
'selected_tools': ['get_lat_long', 'get_weather']}
Test with the find place which would return just the latitude and longitude
config = {"configurable": {"user_id": 9188}}
graph.invoke({"messages": [HumanMessage(content="Find me the place called Seattle")]},config)
invoke_retriever::result=The functions to be called are: get_lat_long::user_message=Find me the place called Seattle::
dynamic_agent::['get_lat_long']
dynamic_agent::['get_lat_long']
{'messages': [HumanMessage(content='Find me the place called Seattle', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='5534f221-f0d7-4ec5-8543-f7c53d5ff4ee'),
AIMessage(content=[{'type': 'text', 'text': 'Here is the latitude and longitude for the place called Seattle:'}, {'type': 'tool_use', 'name': 'get_lat_long', 'input': {'place': 'Seattle'}, 'id': 'tooluse_3WpykM_xS3mpl7mgJcs47A'}], additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={'ResponseMetadata': {'RequestId': '0d844c93-f58f-40ca-b98b-93298b6817af', 'HTTPStatusCode': 200, 'HTTPHeaders': {'date': 'Thu, 28 Nov 2024 22:55:11 GMT', 'content-type': 'application/json', 'content-length': '356', 'connection': 'keep-alive', 'x-amzn-requestid': '0d844c93-f58f-40ca-b98b-93298b6817af'}, 'RetryAttempts': 0}, 'stopReason': 'tool_use', 'metrics': {'latencyMs': 594}}, id='run-248964b5-f495-42e3-b464-8487120bd8d3-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'get_lat_long', 'args': {'place': 'Seattle'}, 'id': 'tooluse_3WpykM_xS3mpl7mgJcs47A', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 343, 'output_tokens': 68, 'total_tokens': 411}),
ToolMessage(content='{"latitude": "47.6038321", "longitude": "-122.330062"}', name='get_lat_long', id='03b1896a-3d31-4642-8e28-3fd7c199d70b', tool_call_id='tooluse_3WpykM_xS3mpl7mgJcs47A'),
AIMessage(content='The latitude for Seattle is 47.6038321 and the longitude is -122.330062.', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={'ResponseMetadata': {'RequestId': 'e1a25f98-010a-49e3-aeb9-73e3251be094', 'HTTPStatusCode': 200, 'HTTPHeaders': {'date': 'Thu, 28 Nov 2024 22:55:12 GMT', 'content-type': 'application/json', 'content-length': '255', 'connection': 'keep-alive', 'x-amzn-requestid': 'e1a25f98-010a-49e3-aeb9-73e3251be094'}, 'RetryAttempts': 0}, 'stopReason': 'end_turn', 'metrics': {'latencyMs': 360}}, id='run-a4d3104c-53b4-4c22-8d4c-b400c3a08a45-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 441, 'output_tokens': 26, 'total_tokens': 467})],
'selected_tools': ['get_lat_long']}
Test with something which is semantically closer to find place
config = {"configurable": {"user_id": 9188}}
graph.invoke({"messages": [HumanMessage(content="Suggest me a good vacation destination.")]},config)
invoke_retriever::result=The functions to be called are: get_lat_long::user_message=Suggest me a good vacation destination.::
dynamic_agent::['get_lat_long']
{'messages': [HumanMessage(content='Suggest me a good vacation destination.', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='aa496893-a8ba-4e8f-9436-211f765ded24'),
AIMessage(content="Okay, let me try to suggest a good vacation destination for you. To do that, I'll first need to get some more information about what you're looking for in a vacation. Could you please provide some details on the following:\n\n- What type of environment or scenery are you interested in (e.g. beach, mountains, city, etc.)?\n- What activities or experiences would you like to have on your vacation (e.g. relaxation, adventure, culture, food, etc.)?\n- How much time do you have for the vacation (e.g. a long weekend, 1 week, 2 weeks, etc.)?\n- What is your budget or price range for the vacation?\n\nWith a few more details about your preferences and constraints, I can try to suggest some great vacation destination options that might be a good fit for you. Let me know what additional information you can provide.", additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={'ResponseMetadata': {'RequestId': '34b9b89e-9e75-4cf2-bc24-b2792787b3a2', 'HTTPStatusCode': 200, 'HTTPHeaders': {'date': 'Thu, 28 Nov 2024 22:54:44 GMT', 'content-type': 'application/json', 'content-length': '999', 'connection': 'keep-alive', 'x-amzn-requestid': '34b9b89e-9e75-4cf2-bc24-b2792787b3a2'}, 'RetryAttempts': 0}, 'stopReason': 'end_turn', 'metrics': {'latencyMs': 2034}}, id='run-5dbf808f-a4b6-498e-99af-637d4ca28621-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 345, 'output_tokens': 196, 'total_tokens': 541})],
'selected_tools': ['get_lat_long']}
Here you can see that the agent correctly searched using an image of amsterdam and returned information about it from our vector store.
Congratulations
You have successfully finished this lab. You can now move over to the next one!