CloudTrail Lake
CloudTrail Lake aggregates, immutably stores, and queries ingested events, offering a managed data lake for your organization. Your organization can use these events for auditing, security investigations and operational investigations. CloudTrail Lake simplifies analysis workflows by integrating collection, storage, preparation, and optimization for analysis and querying within CloudTrail. The following will outline some best practices around CloudTrail Lake.
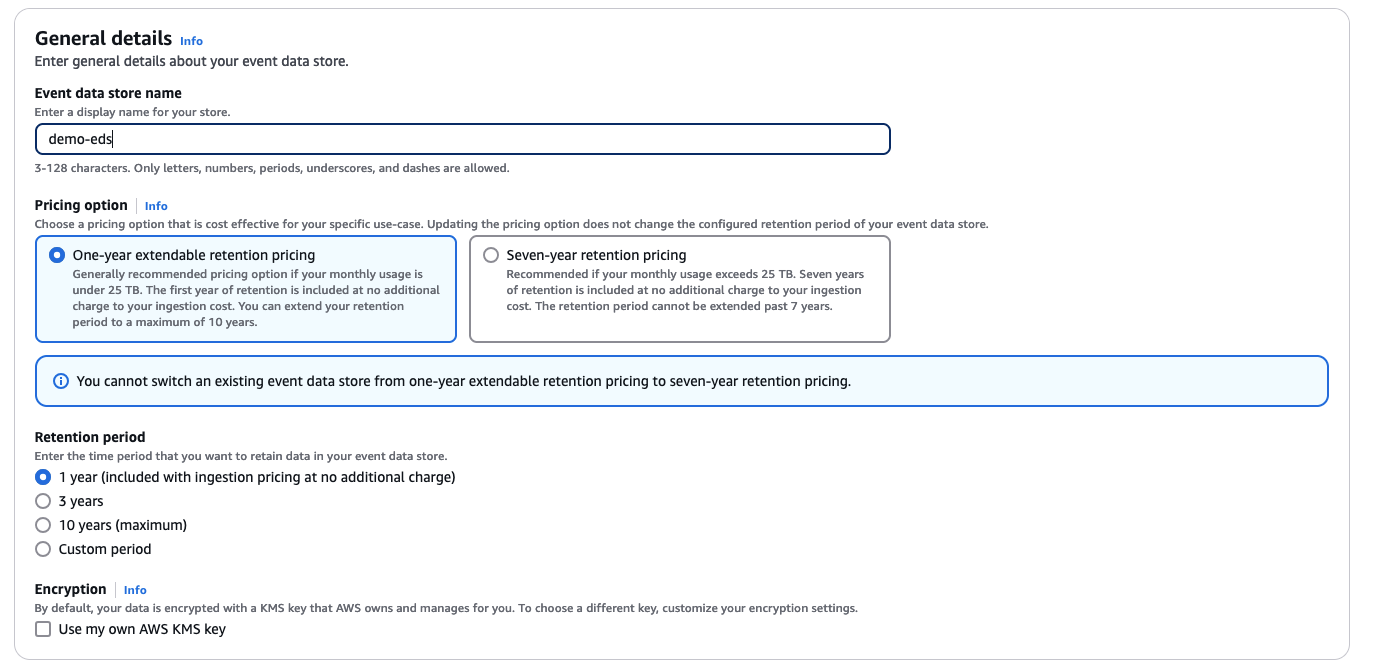
Choosing a right pricing option
When creating your event data store, you want to choose a pricing option that fits the type and amount of events you expect to ingest monthly. For most, the One-year extendable retention pricing option is the most cost-effective approach. However, if you will be ingesting more the 25 TB of data a month, then the Seven-year retention pricing option may be a better choice.
Lake query Federation
We recommend enabling Lake query Federation, which will allow you to configure your event data store for zero-ETL analysis from Athena. This will help removes the operational complexities of building data processing pipelines to be able to correlate activity logs with application logs or Cost and Usage data stored in S3. This will also allow you to run cross join queries within Athena against your other data sets. Enabling this feature will also remove the need to replicate or move your CloudTrail data since it provides a federate link to your event data store using LakeFormation. With this feature you can also use LakeFormation to create data filters and share subset of your data within your event data store to other accounts within your organization. For more information please take a look at the blog: Securely share AWS CloudTrail Lake logs across accounts without replicating data
Configure Resource based policies
You can configure resource based policies to grant permissions to other IAM principals. This would allow you to share your EDS to other member accounts to query the CloudTrail data. This can help avoid the need to duplicate or copy events to other accounts since you can grant specific IAM principles access to query the event data store.
Configure Tags for your event data store
Adding tags to your event data store can allow you to track the query and ingestion costs for your CloudTrail Lake event data if you add these tags as user defined cost allocation tags. Another use case for tags for your event data store would be for adding an resource based IAM policy defining who can manage or query an event data store.
Ingest data events for your event data store
Data events provide visibility into the resource operations performed on or in the resource. CloudTrail data events supports various resource types for a full list of supported resource types, please take a look at the doc CloudTrail data events. These events are also known as data plane operations. Data events are often high-volume activities, especially if you are storing sensitive data on S3 or have key business operations occurring through Lambda functions. Visibility into any unexpected access to sensitive data lets you take corrective action to protect your data. Because some compliance reports (for example, FedRAMP and PCI-DSS ) require data events to be turned on, AWS recommends that you use AWS Config managed rules or an appropriate Conformance Pack Sample Templates to check that at least one trail is logging S3 data events for all S3 buckets.
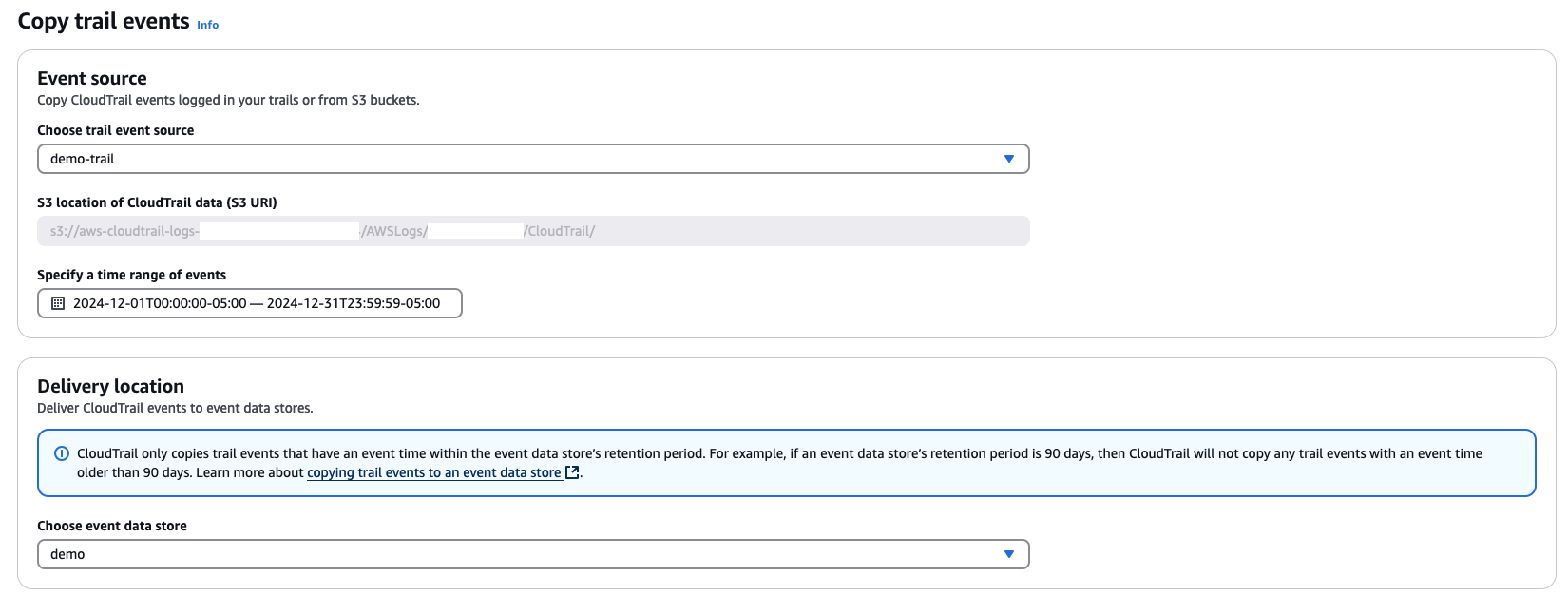
Import historical CloudTrail Trail events
When migrating from CloudTrail Trails to CloudTrail Lake, use the Copy Trail event feature to copy existing trail events to your CloudTrail Lake event data store which were recorded prior to event data store creation. This will allow you to import events from an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets corresponding to a CloudTrail trail into a CloudTrail Lake EDS. However, when using this feature its recommended to specify an import date range, so that you only import the subset of logs that are needed for long-term storage and analysis in Lake. This will help prevent additional costs related to importing of logs outside of the date range specified.
Enhanced filtering options for CloudTrail events ingested into event data stores
Enhanced event filtering capabilities give you greater control over which CloudTrail events are ingested into your event data stores. These enhanced filtering options provide tighter control over your AWS activity data, improving the efficiency and precision of security, compliance, and operational investigations. Additionally, the new filtering options help you reduce your analysis workflow costs by ingesting only the most relevant event data into your CloudTrail Lake event data stores.
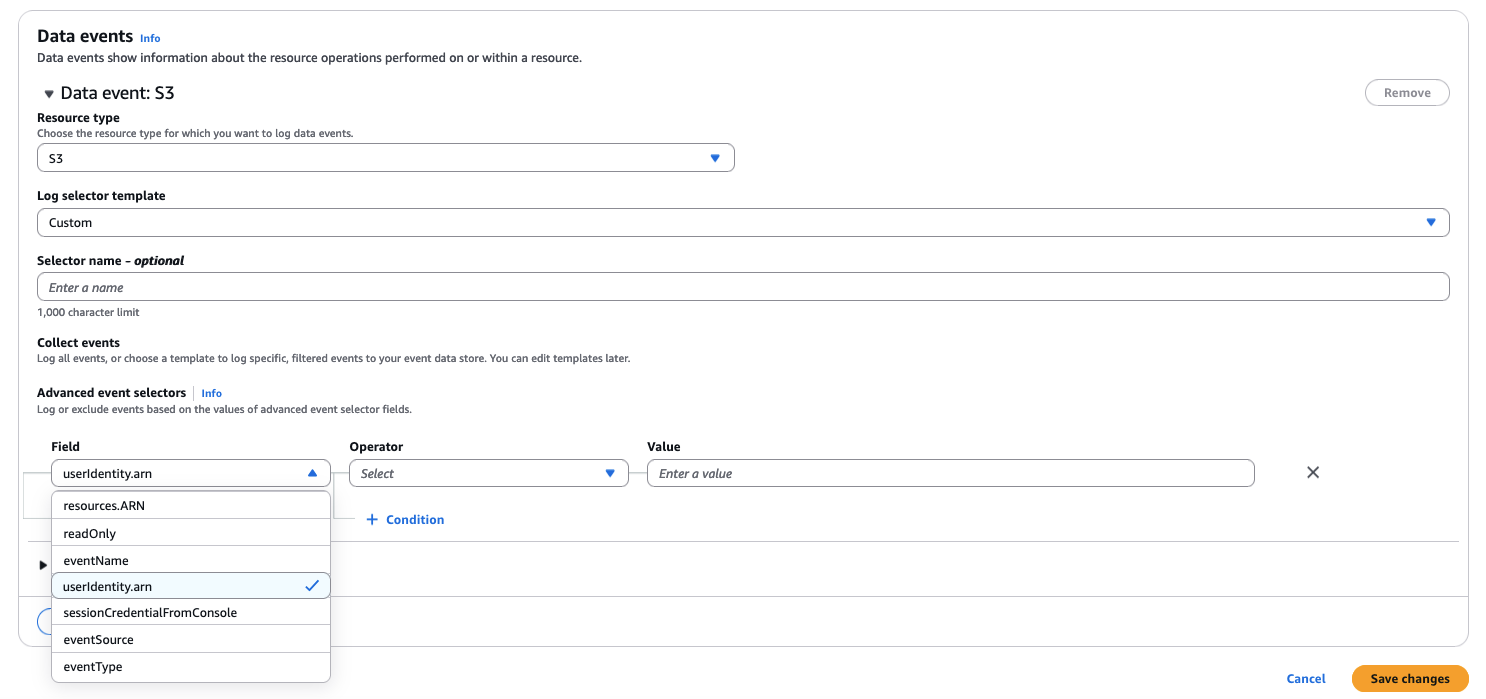
You can filter management events by using the Advanced Event Collection and filter events to included or excluded based on attributes such as eventSource, eventType, eventName, userIdentity.arn, and sessionCredentialFromConsole.
When you use data events, we recommend using advanced event selectors which offer greater control over which CloudTrail events are ingested into your event data stores. With advanced event selectors, you can include or exclude values on fields such as EventSource, EventName, userIdentity.arn, and ResourceARN. Advanced event selectors also support including or excluding values with pattern matching on partial strings.
Using enhanced filters for CloudTrail will help increase the efficiency and precision of your security, compliance, and operational investigations while helping reduce costs. For example, you can filter CloudTrail events based on the userIdentity.arn attribute to exclude events generated by specific IAM roles or users. You can exclude a dedicated IAM role used by a service that performs frequent API calls for monitoring purposes. This allows you to significantly reduce the volume of CloudTrail events ingested into CloudTrail Lake, lowering costs while maintaining visibility into relevant user and system activities.
SQL Queries
When running SQL queries, we recommend that you constrain queries by adding starting and ending eventTime time stamps to queries. This will help minimize the cost when data is scanned for queries. You can do this by adding the eventtime field in the where clause, adding time range that will be searched with the time range you want to use. The date string specified after eventTime > is the earliest event timestamp that will be included, while the date string specified after eventTime < is the latest event timestamp that will be included. The following query is a sample showing the usage of the eventtime field.
SELECT eventTime, useridentity.arn, awsRegion FROM $EDS_ID WHERE eventTime > '2024-07-20 00:00:00' AND eventTime < '2024-07-23 00:00:00' AND awsRegion in ('us-east-1') AND eventName = 'ConsoleLogin'
Natural language prompts
Use the Natural Language query processor to help you get started in analyzing your activity logs (management and data events) stored in CloudTrail Lake without having to write a SQL query or spend time in understanding the SQL syntax needed to query your activity events. NLQ can also be helpful you to get quicker insights into your data by asking what you would like to query and then it providing the SQL query to use.
CloudTrail query results integrity validation
CloudTrail Lake query results integrity validation lets you know if the query results where modified, deleted or changed when the results were exported. By validating the query results, allows you to asset that no changes were made to the exported results file delivered by CloudTrail. To validate the results, you can use the verify-query-results AWS cli command to verify the hash value of each query result file to the hash value in the signed file.
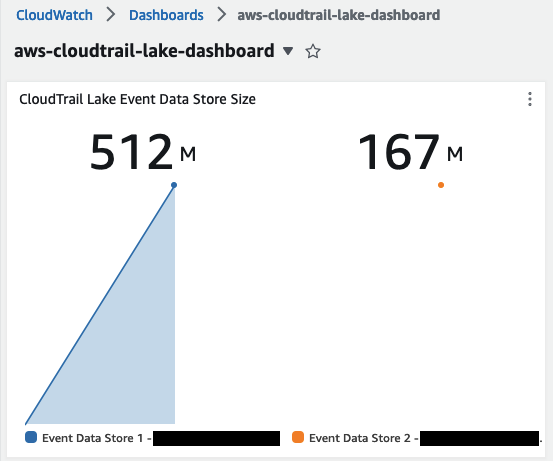
Setup CloudWatch alerts to monitor CloudTrail Lake usage
You can create alarms and notification on the supported CloudWatch metrics for CloudTrail Lake to help track your event data store usage over a period of time. You can then setup alerts to notify you when it has passed a certain threshold. With CloudWatch you can mornitor metrics such as HourlyDataIngested, TotalDataRetained, TotalStorageBytes & TotalPaidStorageBytes to help you gain further visibility to your overall data usage for CloudTrail Lake. For example, you can create a CloudWatch Dashboard showing you CloudTrail Lake Event Data Store Size.
SORT(SEARCH('{AWS/CloudTrail,"Event data store ID","Lake Metrics"} MetricName="TotalPaidStorageBytes" NOT "Lake Metrics"="IngestionMetrics"',"Sum"),SUM, DESC)
CloudTrail Lake Dashboards
We recommend enabling CloudTrail Lake dashboards to visulize your event trends of the data stored in your event data stores in CloudTrail Lake. The Highlights dashboard will provide an overall easy-to-view summary of the data captured in CloudTrail Lake. This will provide a dahsboard to quickly identify and understand important insights within your event data store, such as the top failed API calls, trends in failed login attempts, and spikes in resource creation. The CloudTrail Lake dashboards also provide other managed dashboards specific to an AWS service that will provide further insights around this service. You can also create a custom dashboard showing your own widgets or specific widgets from any of the managed dashboards.