Automation
With Automation, a capability of AWS Systems Manager, you can author custom runbooks with a low-code visual designer, or choose from over 370 predefined runbooks provided by AWS across multiple accounts and AWS Regions. You can run Python or PowerShell scripts as part of a runbook in combination with other Systems Manager Automation actions such as approvals, AWS API calls, or running commands on your nodes.
Automation can enable businesses to improve performance by reducing errors, improving resiliency. Automation can enhance both security and operations in various ways, here some examples:
- Configuration Management: Automation tools can enforce standardized configurations across servers, workstations, and network devices, reducing the likelihood of misconfigurations that could lead to security vulnerabilities.
- Patch Management: Automation can be used to deploy security patches and updates across systems, reducing the window of vulnerability to known exploits.
- Incident Response Playbooks: Automation can execute predefined incident response playbooks to guide security teams through the steps needed to contain, investigate, and remediate security incidents. Application owners can create an Automation runbooks to respond to systems outage incidents. For example, loss of network connectivity, software issues on the physical host, loss of system power. Using Amazon CloudWatch alarms to stop, terminate, reboot, or recover an EC2 instance.
- Compliance Management: Automation can assist in maintaining compliance with industry regulations and internal policies by automating audit processes, generating compliance reports, and enforcing security controls consistently.
By leveraging Systems Manager Automation, you can streamline this critical process, ensuring that your application servers remain up-to-date and compliant with your organization's security policies. This not only saves time and reduces the potential for manual errors, but also provides a consistent and repeatable approach to this recurring task.
Managing permissions using service role
As a security best practice, you can create an IAM role ( assumable by SSM service) to start the automation. When you use a service role, the automation is allowed to run against the AWS resources, but the user who ran the automation has restricted access (or no access) to those resources.
Elevated security and control - Delegated administration ensures elevated security and control of your AWS resources. If you want to modify the permissions, make those changes at the service role instead of multiple IAM accounts.
Enhanced auditing experience - Allows an enhanced auditing experience because actions are being performed against your resources by a central service role instead of multiple IAM accounts.
The following situations require that you specify a service role for Automation: 1/ When you want to use delegated administration. 2/ When you create a Systems Manager State Manager association that runs a runbook. 3/When you have operations that you expect to run longer than 12 hours. 4/ When you're running a runbook not owned by Amazon that uses the aws:executeScript action to call an AWS API operation or to act on an AWS resource.
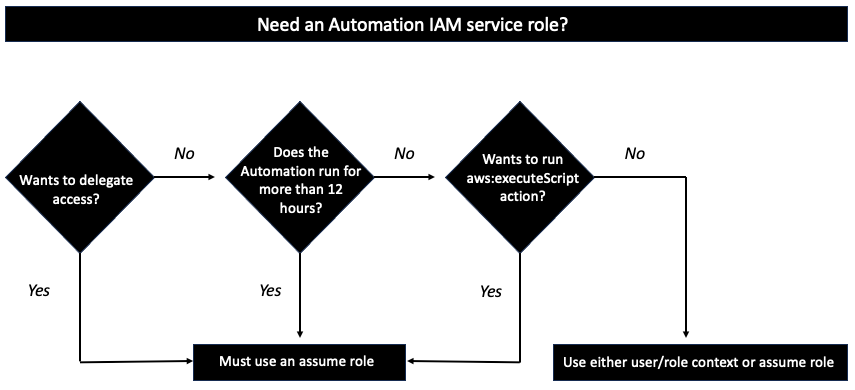
After creating your service role, we recommend editing the trust policy to make sure only Systems Manager Automation in that account is allowed to assume the role. For the role policy, attach only required permission to run the automation actions defined in the runbook. The IAM entity that starts the automation is allowed to start the required automation runbooks. The entity is allowed to pass the automation service role to Systems Manager. This entity is not granted permissions to interact with AWS resources directly. Those permissions are delegated to the service role.
- Service role trust policy
- Assumable by Systems Manager
- Service role policy – Least access policy
- Grant only required permission to run the automation actions
- IAM User/Group/Role policy
- Allow to pass the service role to automation
- Allow permissions to start/stop/describe Automation executions
- No permissions required to manage resources outside Automation
Creating Automation runbooks
There are multiple ways to create your own automation runbooks. To create the document programmatically, you can use the CreateDocument API, or using the SSM Documents CDK library. You can also create the document using CloudFormation.
AWS Systems Manager Automation provides a low-code visual design experience that helps you create automation runbooks. The visual design experience provides a drag-and-drop interface with the option to add your own code so you can create and edit runbooks more easily.
As you create a runbook, the visual design experience validates your work and auto-generates code. You can review the generated code, or export it for local development. When you're finished, you can save your runbook, run it, and examine the results in the Systems Manager Automation console.
In the visual design experience, Automation integrates with Amazon CodeGuru Security to help you detect security policy violations and vulnerabilities in your Python scripts.
Options available:
- Leverage AWS APIs or create documents using CloudFormation
- Visual design experience for Automation runbooks
- Visual Studio Code Toolkit
- CDK for Systems Manager Documents
Systems Manager allows runbooks to be shared across AWS accounts. This enables effective collaboration and promotes the adoption of best practices. For example, a central account can define security best practices as automation runbooks and share them with other accounts within the organization. This ensures consistent implementation of security measures across the entire AWS environment.
By default SSM doesn't support sharing runbooks using an AWS Organization Unit (OU). There is a solution available to workaround this limitation.
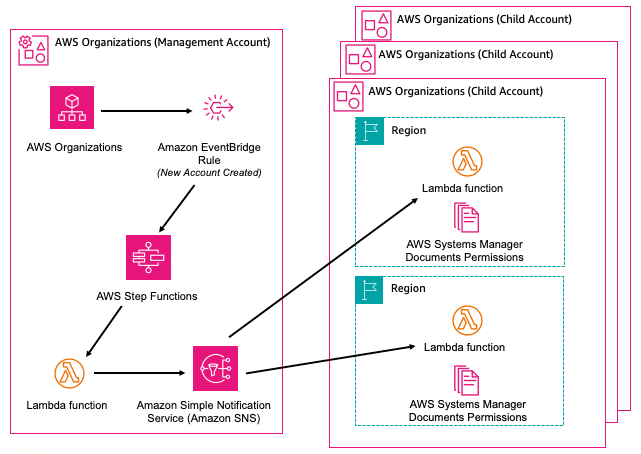
The solution uses several AWS resources, including an EventBridge Rule, Lambda functions, a Step Function State Machine, and an SNS topic. Once deployed, the solution will trigger a workflow each time a new account is added to an AWS Organizations via the CreateAccount or InviteAccountToOrganization API call. The workflow will add SSM Document share permissions for the newly added Account ID in a designated AWS Organizations child account and all specified Region(s). Learn more on Automate AWS Organizations SSM Document Share Permissions.
Running Automation
- Simple Automation – Current region & account
- Manual Automation – Interactive step-by-step execution. Each step executed manually. Useful for troubleshooting purpose.
- Multi Account Multi Region Automation – Run automation across multiple AWS Regions and AWS accounts or AWS Organizations organizational units (OUs) from a central account.
- Run at scale – Target using Tags, Resource Groups or Parameter values
- Rate Control – Concurrency & Error threshold. Controls blast radius. The concurrency value determines how many resources are allowed to run the automation simultaneously.
- Adaptive Concurrency – Up to 500 concurrent automations. Enable it in Automation preferences.
- CloudWatch Alarm Integration – Attach CloudWatch alarm to monitor automation. If the alarm activates, automation is stopped.
- Security – IAM access control.
- Using IAM policies , administrators can control which individual users or groups in your organization can use Automation and which runbooks they can access.
- Automation allows access delegation using IAM service role. When you use a service role, the automation is allowed to run against the AWS resources, but the user who ran the automation has restricted access (or no access) to those resources.
Running Automation in multiple accounts and Regions
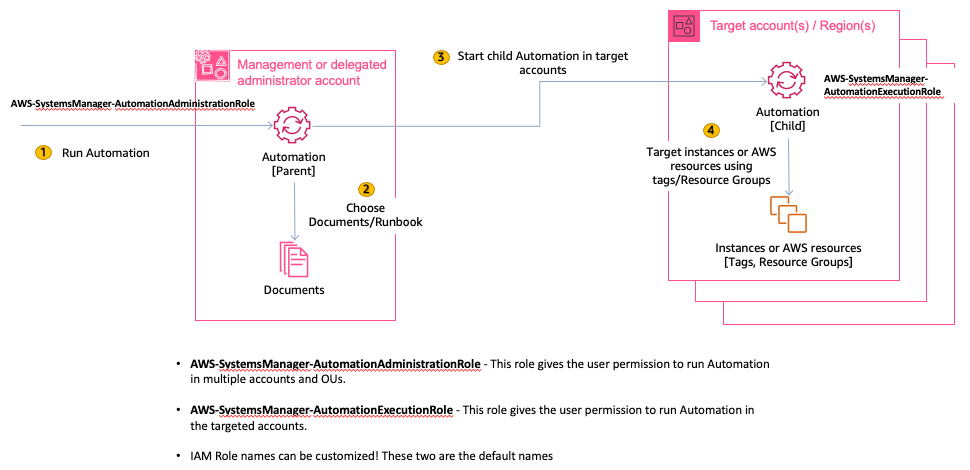
Running automations across multiple Regions and accounts or OUs works as follows:
- Verify that all resources on which you want to run the automation, in all Regions and accounts or OUs, use identical tags. If they don't, you can add them to an AWS resource group and target that group. For more information, see What are resource groups? in the AWS Resource Groups and Tags User Guide.
- Sign in to the account that you want to configure as the Automation central account.
- Use the Setting up management account permissions for multi-Region and multi-account automation procedure in this topic to create the following IAM roles:
- AWS-SystemsManager-AutomationAdministrationRole - This role gives the user permission to run automations in multiple accounts and OUs.
- AWS-SystemsManager-AutomationExecutionRole - This role gives the user permission to run automations in the targeted accounts.
- Choose the runbook, Regions, and accounts or OUs where you want to run the automation.
Considerations for multi-account/Region Automation:
- When targeting Resource Groups, the resource group must exist in each target account and Region
- The resource group name must be the exact same in each target account and Region
- Automations does not run recursively through OUs
- Automation can only target OUs which contain accounts
- Recommend customers to create the required IAM roles for multi-account/Region using CloudFormation or IaC