Patching managed nodes using AWS Systems Manager and tagging
Introduction
Maintaining security and performance across your node infrastructure requires a robust patch management strategy. This guided solution will walk you through implementing an automated, tag-based patch management system using AWS Systems Manager. By following this guided solution, you will establish a scalable and efficient patching process that reduces manual intervention while improving security compliance. This method can be utilized within AWS Organizations for a centralized approach, and can be implemented for single accounts as well.
Utilizing a tagging scheduling method such as this can allow the application owners to manage when their nodes receive updates. Approved schedules, which would have a corresponding patch policy, can be queried using the AWS CLI, allowing for a self-service method of changing of a nodes schedule.
Understanding the solution
Before you begin to implement certain parts into your patch management solution, it's important to understand how this solution works. The approach combines AWS Systems Manager's patch management capabilities with a standardized tagging strategy. This integration allows you to automate patching schedules across your managed nodes while maintaining granular control over update schedules.
Each managed node would be assigned a predefined tag, in this case, maintenance:patching. The value of this tag would contain an entry similar to a cron expression, which would indicate the schedule the node would be evaluated and have updates applied.
Patch policies would be created to match each of the authorized schedules that managed node should receive updates.
Custom patch baselines can be created and associated to the patch policies, allowing for additional control over the updates that are applied or the default patch baselines can be utilized.
Once the patch policies and tags are established and assigned, the managed nodes will have the patch policies applied as per the specifications within the patch policies and patch baselines.
Role-based responsibilities
Cloud Operations team
The Cloud Operations team plays a crucial role in maintaining the security and stability of our cloud infrastructure through comprehensive patch management oversight. Their responsibilities encompass several key areas that ensure the effectiveness of our patching program.
Continuous monitoring of patch deployment success rates is essential to maintaining system health. The team leverages AWS Systems Manager to track and analyze patching outcomes, generating weekly reports to identify patterns and potential areas of concern. (See Working with patch compliance reports) This proactive monitoring enables early detection of systemic issues and ensures patches are applying successfully across the environment.
The team maintains responsibility for the automation infrastructure that drives our patching process. This includes regular refinement of AWS Systems Manager patch baselines, optimization of deployment schedules, and maintenance of automation workflows. These automated processes must be continuously evaluated and adjusted to accommodate changing business needs while maintaining security standards.
When patching failures occur, the Cloud Operations team serves as the primary responder. They must investigate issues within 24 hours, coordinate necessary remediation efforts, and work with application teams when required. Thorough documentation of incidents and their resolutions helps build a knowledge base for future reference and drives continuous improvement of the patching process.
Regular compliance oversight represents another critical responsibility. The team conducts weekly reviews of patching tag compliance, ensuring all nodes adhere to established standards. This includes verifying proper tag implementation and managing any necessary remediation through AWS Config rules. They maintain detailed records of compliance status and manage any approved exceptions to standard processes.
Through these activities, the Cloud Operations team ensures a robust and reliable patching program that maintains system security while minimizing business impact. Their role as the escalation point for patching issues and their ongoing communication with stakeholders helps maintain transparency and trust in the patching process.
Security team
The Security team serves as the governance authority for our managed node patching program, ensuring that security standards are maintained and compliance requirements are met through comprehensive oversight and strategic direction.
Patch compliance monitoring forms a cornerstone of the Security team's responsibilities. Through regular analysis of compliance reports, they evaluate the organization's security posture and identify potential vulnerabilities that require attention. This oversight includes reviewing patch deployment metrics, analyzing security advisory impacts, and ensuring critical patches are being applied within required timeframes.
The team maintains and evolves security requirements based on emerging threats and industry best practices. When new vulnerabilities are discovered or compliance standards change, they assess the impact and update patching requirements accordingly. This includes defining acceptable patch deployment windows, establishing minimum compliance thresholds, and determining which security patches must be prioritized.
Patch baseline governance falls under their purview, with the Security team serving as the approval authority for modifications to patch baselines. They evaluate proposed changes against security standards and compliance requirements, ensuring that any adjustments maintain an appropriate security posture while accommodating operational needs. This includes reviewing both operating system and application patch specifications.
The team conducts regular compliance validations to verify that patching processes align with regulatory requirements and internal security policies. They maintain documentation of compliance status, manage audit responses, and provide guidance on remediation when gaps are identified. Their assessment helps ensure the organization maintains its security certifications and meets its compliance obligations.
Through these activities, the Security team establishes and maintains the security framework that guides our patching program, ensuring that security remains a primary focus while enabling operational efficiency.
Application teams
Application teams play a vital role in ensuring successful patch management while maintaining application availability and performance. Their intimate knowledge of application behavior and business requirements makes them essential participants in the patching process.
Coordination of patching schedules requires careful consideration of business operations. Application teams must work proactively with Cloud Operations to identify suitable schedules that minimize business impact. They need to assess peak usage periods, critical business events, and dependencies to determine when patching can safely occur.
Post-patching validation is a critical responsibility where application teams must systematically verify their applications' functionality. Following each patch cycle, they should execute established testing procedures to confirm that all critical business functions operate as expected. This includes monitoring application performance metrics, validating core functionality, and verifying integrations with dependent systems remain intact.
When issues arise, application teams must follow established escalation procedures to ensure proper incident tracking and resolution. This includes providing detailed documentation of any observed problems, including specific symptoms, timing of issues, and potential correlation with recent patches. Timely and accurate reporting helps Cloud Operations and Security teams respond effectively to patch-related incidents.
Resource tagging accuracy falls squarely within the application team's responsibilities. They must maintain current and accurate tags on all their resources, particularly those related to patching schedules. These tags drive automated patching processes, and their accuracy is crucial for ensuring systems are patched according to the appropriate schedule and requirements.
Through these responsibilities, application teams serve as the essential bridge between technical operations and business needs, ensuring that patching activities maintain system security while preserving application availability and performance.
Building the foundation
Prerequisites for tag-based patching implementation
AWS Systems Manager configuration
AWS Systems Manager must be properly configured at the account or organizational level before implementing tag-based patching. In an organizational context, ensure Systems Manager is enabled across all relevant accounts through AWS Organizations. Configure appropriate IAM roles and policies to allow Systems Manager to manage resources, including the required service-linked roles and instance profiles. Establish resource data sync if centralized visibility across multiple regions or accounts is needed.
SSM Agent management
All managed nodes must run a properly configured SSM Agent. While many AWS AMIs include the agent by default, verify it is present and updated to the latest version. For non-AWS managed nodes, implement a process to install and configure the agent during instance provisioning. Establish an automated process to maintain agent updates, leveraging Systems Manager's agent auto-update capability where appropriate.
Network connectivity requirements
Systems Manager requires consistent network connectivity to manage nodes effectively. Ensure managed nodes can reach Systems Manager endpoints either through the internet or through VPC endpoints. For nodes in private subnets, configure the necessary VPC endpoints for Systems Manager (ssm, ssmmessages, and ec2messages). Verify security groups and network ACLs permit the required traffic. If using a proxy, configure the SSM Agent with appropriate proxy settings.
Patch tagging strategy
Develop and document a comprehensive tagging strategy that aligns with organizational needs. Define:
- Tag key-value pairs for identifying patch groups (e.g.,
maintenance:patching) - Tag enforcement mechanisms through AWS Config rules
- Tag governance and ownership responsibilities
- Procedures for tag updates and modifications
Document the complete tagging schema, including any variations needed for different environments or application types. Establish processes for validating tag compliance and remediating improperly tagged resources.
Network connectivity to the patch source or repositories will be required as well. Please see Connectivity to the patch source for more information.
Implementing the patching process
Keeping your managed nodes up-to-date and secure is an important part of maintaining your AWS, on-premises, and multi-cloud infrastructure. With AWS Systems Manager, you can automate many security and other types of software updates (patches) across your managed node fleet. However, managing patching schedules and cadences can still be complex, especially as your infrastructure scales. This guided solution is an example of one method that can be employed to assist in managing patching schedules with flexibility.
Step 1: Establishing your tagging strategy
Begin by implementing the maintenance:patching tagging convention. This tag will define when patches should be applied to each node. The tag value uses a cron-like expression to specify the schedule. It is common for organizations to select off hour (non production) times to apply updates. In cases like these, select times and days of the month can be chosen as standards that each node would need to align with.
For example:
Key: maintenance:patching
Value: 2SATX4 # Runs at 2 AM every 4th Saturday
The 'X' in the value is used to replace the '#' symbol, which is not within the allowed characters for a tag values
Other common patterns for the values include:
0SUNfor every Sunday, midnight maintenance4TUEX2for every 2nd Tuesday, 4 AM maintenance22MONX3for every third Monday, 10 PM maintenance
The following diagram demonstrates how tags on managed nodes, from various sources, can align with a patch policy.
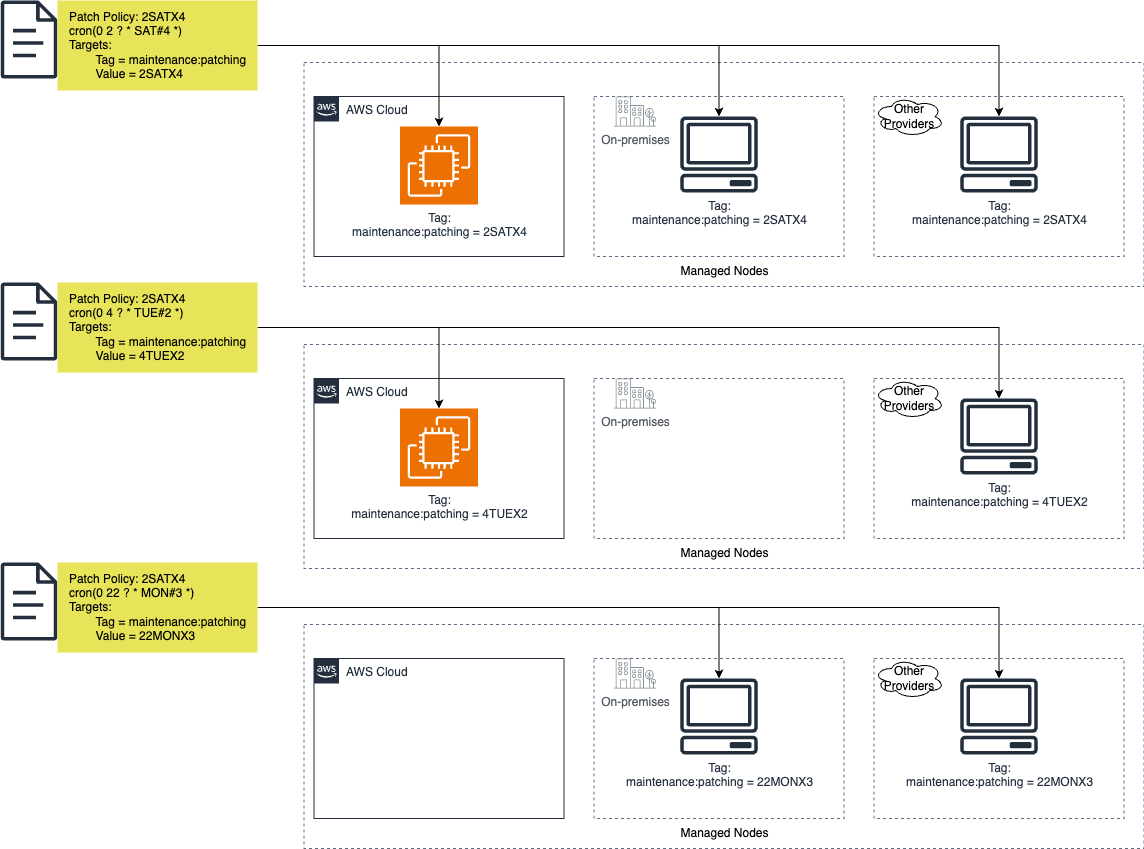
One implementation of this solution provided implementation times beginning on Friday evenings at 10 PM. Subsequent time offerings were created for every four hours after 10 PM Friday until 10 PM Sunday. This allowed for 13 options weekly for updates to be applied that could be spread across the environment as needed, including the ability to update environments such as development, test, and production on separate schedules.
Step 2: Deploying your tag strategy
Once you have decided on your tagging strategy, you will want to ensure that your existing nodes receive the new required tag and enact standards requiring the tag on all new nodes.
Compliance enforcement
Implement AWS Config rules to maintain tag governance across your environment. Configure rules to verify the presence of required patching tags on all managed nodes and validate that tag values conform to approved standards. This automated oversight ensures consistent tagging across your infrastructure and helps identify non-compliant resources quickly.
Automated remediation
Establish automated remediation processes using AWS Systems Manager Automation to address non-compliant resources. Your remediation workflow should add missing tags with appropriate default values based on resource characteristics. Design your remediation to be both automatic for standard cases and manual for exceptions that require human review.
Audit and review process
Deploy AWS Config rules to automatically monitor managed nodes for the maintenance:patching tag, ensuring both tag presence and valid patching schedule values (e.g., 2SATX4, 4TUEX2). Review Config compliance reports weekly to identify non-compliant resources and validate that auto-remediation is functioning properly. Create and maintain documentation of approved exceptions in a centralized location.
Governance model
Establish clear ownership and responsibilities for tag management, with Cloud Operations maintaining approved patching schedules in AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store for consistent reference across the organization. Define processes for requesting changes to tag standards and patching schedules, ensuring updates are reflected in both Parameter Store and associated Config rules. Create documented approval workflows for changes, requiring Security team validation before Cloud Operations updates the centralized parameters. Maintain feedback loops between operations, security, and application teams to ensure the tagging strategy and maintenance windows continue to meet organizational needs, using Parameter Store as the source of truth for approved values.
Step 3: Configuring Systems Manager
With your tagging strategy in place your Cloud Operations Team can configure Systems Manager to execute your patching strategy:
Patch baseline guidance
Before creating a custom patch baseline, evaluate whether AWS's predefined baselines meet your patching requirements. Review the default AWS-managed baselines for your operating systems, which typically include approved patches for critical updates and security patches. If your organization has specific compliance requirements, patch exclusions, delayed patch approvals, or needs to manage particular application dependencies, you'll likely need a custom baseline. However, if you simply need to apply critical and security updates on a regular schedule, the AWS-managed baselines often provide sufficient coverage while requiring less maintenance overhead. Document your patching requirements and compare them against the predefined baseline configurations to make an informed decision.
Patch policy configuration guidance
For each approved patching schedule defined in Parameter Store, create a corresponding patch policy in AWS Systems Manager. Name your policy to clearly reflect its CRON schedule, ensuring easy correlation with patching schedules (e.g., Patch-2SATX4). Configure the policy for both scan and install operations, utilizing the Custom Scan schedule option to specify your pre-approved CRON expression that aligns with the patching schedule.
When defining the policy's scope, select your designated patch baseline and configure targeting using the Custom Targets option. Specify the appropriate organizational units (OUs) and AWS regions where this policy should apply. Most critically, set the target nodes using the maintenance:patching tag, entering the specific tag value that corresponds to this patching schedule (e.g., 2SATX4). This ensures that only nodes explicitly tagged for this patching schedule will be included in the patching operation.
This configuration approach maintains consistency between your tagging strategy, patching schedules, and patch policy execution, while providing clear visibility into which nodes will be patched during each scheduled period.
Automation workflow guidance (optional)
Enhance your patching strategy by implementing supplemental automation workflows in AWS Systems Manager. Design pre-patch validation checks to verify system readiness, such as confirming available disk space, running process verification, and backing up critical configurations. Create post-patch testing automation to validate system functionality, including service status checks, application health monitoring, and basic connectivity tests. Configure SNS topics and notification pathways to alert appropriate teams of patch execution status, test failures, or validation issues. These automated workflows strengthen your patching process by providing consistent validation and clear communication channels throughout the patch cycle.
Implementation roadmap
Follow these steps to roll out your patching strategy:
Phase 1: Planning and design (Weeks 1-2)
This foundational phase helps customers establish a clear understanding of their current environment and set achievable goals. The detailed documentation and role definitions ensure accountability and smooth operations across teams. By establishing standardized tagging and automation workflows upfront, organizations can achieve consistent and efficient patch management while minimizing human error. This phase creates the framework for maintaining compliance and security standards while reducing operational overhead.
- Assess and document the current environment's patch management state
- Define measurable success criteria including compliance targets and reporting requirements
- Establish tag standards, including approved patching schedule values to be stored in Parameter Store
- Design automation workflows for pre-patch validation and post-patch testing (optional)
- Document roles and responsibilities for Cloud Operations, Security, and Application teams
Phase 2: Testing and validation (Weeks 3-4)
Testing in a controlled environment allows customers to identify and resolve potential issues before they impact production systems, significantly reducing business risk. The validation process ensures that automated workflows function as intended and that reporting provides the necessary visibility into patch status and compliance. This phase helps organizations refine their procedures and build confidence in their patch management strategy while maintaining system stability and security. The thorough testing across different configurations ensures that the solution works reliably across the entire infrastructure.
- Deploy AWS Config rules for tag compliance monitoring in test environment
- Implement patch policies with associated automation workflows
- Validate tag enforcement and auto-remediation processes
- Verify reporting mechanisms and dashboard effectiveness
- Conduct thorough testing across different instance types and operating systems
- Review and adjust procedures based on test results
Phase 3: Production implementation (Weeks 5-6)
The phased rollout approach minimizes business disruption while ensuring successful implementation across the production environment. Regular monitoring and documentation of issues helps create a knowledge base for future reference and continuous improvement of the patch management process. Stakeholder reviews and finalized documentation ensure that the solution meets business requirements and can be effectively maintained long-term. This phase establishes a sustainable, automated patch management system that reduces manual effort while maintaining security and compliance standards.
- Execute phased rollout starting with non-critical application tiers
- Monitor Config compliance reports and remediation success rates
- Document encountered issues and resolutions
- Adjust automation workflows and procedures based on production experience
- Conduct stakeholder reviews of patch execution results
- Finalize operational documentation and handover procedures
Each phase includes regular checkpoints with stakeholders to ensure alignment with business requirements and security standards.
Monitoring and maintenance
Ongoing operational processes
Weekly patch compliance review
Conduct weekly reviews of AWS Config compliance reports, Amazon Athena reports, or Amazon QuickSight to identify non-compliant nodes and remediation effectiveness. Cloud Operations team to verify patch policy execution results and address any failed patching attempts. Generate and distribute compliance status reports to stakeholders, highlighting trends and potential issues requiring attention.
Monthly tag accuracy audit
Perform monthly validation that maintenance:patching tags align with approved values in Parameter Store. Review Config rule reports for unauthorized tag modifications and verify auto-remediation is functioning correctly. Document and investigate any patterns of repeated non-compliance, updating procedures if systematic issues are identified.
Quarterly patch baseline assessment
Security team to review and update patch baselines quarterly, ensuring they align with current security requirements and vendor recommendations. Validate that approved patches meet compliance standards and evaluate any excluded patches for risk. Update baseline documentation and communicate changes to stakeholders.
Semi-annual process review
Conduct comprehensive review of the entire patching program twice yearly. Evaluate effectiveness of automation workflows, timing of patching schedules, and overall compliance rates. Gather feedback from all stakeholders and implement process improvements. Update documentation and training materials to reflect any changes to the program.
Each review process includes formal documentation of findings and actions taken, with results shared with appropriate stakeholders.
Troubleshooting and support
Organizations should develop and maintain comprehensive troubleshooting documentation for common patching issues encountered in their environment. Create detailed runbooks for support teams that address, at minimum, the following scenarios:
- Failed patch installations: Document common failure patterns, required log collection procedures, and escalation paths when patches consistently fail.
- Missed patch schedule windows: Provide guidance for identifying root causes of missed schedules and procedures for rescheduling patches appropriately.
- Missing reboot verification: Include steps to validate reboot requirements, procedures for handling stuck reboot states, and guidance for forced reboot scenarios when necessary.
- Tag compliance failures: Document procedures for investigating non-compliant resources, steps to correct tag issues, and methods to verify remediation success.
- Systems Manager connectivity issues: Detail troubleshooting steps for agent connectivity problems, including network validation and IAM permission verification.
Maintain these documents in a centralized location accessible to support teams, and establish a regular review cycle to keep troubleshooting procedures current with environment changes and newly discovered issues.
Additional resources
Maintain links to:
- AWS Systems Manager documentation
- Internal troubleshooting guides
- Contact information for support teams
- Relevant AWS service documentation
Remember to review and update this guide regularly as AWS services evolve and your organization's needs change. Regular feedback from teams using this process will help refine and improve your patching strategy over time.
This standardized approach to patch management will help ensure your managed node fleet remains secure and up-to-date while minimizing operational overhead and potential human error.