Managing SSM Agent within an AWS Organization
This section outlines how to manage SSM agent installation within an AWS Organization and provides sample code CloudFormation, Terraform, Shell, PowerShell, Ansible, Chef, and Puppet.
Please keep in mind that this is sample code and should be thoroughly tested and validated in a development environment prior to any usage in a production environment.
Understanding SSM Agent
As discussed in the previous sections, to get started with managing your nodes in your environment using Systems Manager, nodes must be managed, which means SSM Agent is installed on the machine and the agent can communicate with the Systems Manager service endpoints with required permissions.
AWS Systems Manager Agent (SSM Agent) is Amazon software that runs on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances, edge devices, on-premises servers, and virtual machines (VMs). The source code for SSM Agent is available on GitHub. SSM Agent makes it possible for Systems Manager to update, manage, and configure these resources. The agent processes requests from the Systems Manager service in the AWS Cloud, and then runs them as specified in the request.
Therefore, ensuring the SSM Agent is installed on nodes is necessary and the very first step to address when starting the journey with node management operations using the AWS Systems Manager service.
Operating system support
SSM Agent is supported on a wide range of operating systems and machine types. See Supported operating systems and machine types in User guide to verify that your operating system (OS), OS version, and machine type are supported.
AMIs with SSM Agent pre-installed
To get started with Systems Manager, AWS Systems Manager Agent (SSM Agent) is preinstalled on some Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) provided by AWS and trusted third-parties. See Find AMIs with the SSM Agent preinstalled, to get the list of operating systems where its preinstalled.
SSM Agent installation methods
Now that we understand which operating systems support SSM Agent, let's explore the various methods to install the agent on instances which do not have SSM Agent preinstalled. The installation approach can be categorized into two main scenarios:
- New instance deployment: Installing SSM Agent when launching new instances.
- Existing instance management: Installing SSM Agent on already running instances.
Installing SSM Agent on new instances
When launching new instances, incorporating SSM Agent installation into your initial setup process ensures consistent management capabilities from the start. This approach eliminates the need for post-deployment installation. You can achieve this through various methods such as Golden AMIs, user data scripts, or infrastructure as code tools etc. The choice of method often depends on your organization's deployment practices and scaling requirements.
Golden AMI Approach
A Golden AMI is a customized Amazon Machine Image that serves as a standardized template for launching EC2 instances. For Systems Manager integration, organizations can create Golden AMIs with SSM Agent pre-installed, ensuring all instances launched from these AMIs are immediately manageable through Systems Manager. This approach eliminates the need for post-launch installation scripts and reduces the risk of deployment failures.
Creating a Golden AMI
- Manually: Creating a Golden AMI manually can be done by launching an instance, installing and configuring SSM Agent, testing the configuration, and then creating an AMI from that instance.
- EC2 Image builder: If you are using EC2 Image Builder for creating golden images, configure the image recipe and select the option to keeps the SSM agent in the output image.
- Hashicorp Packer: If you are Hasicorp Packer, use the shell Packer provisioner to run shell commands to install SSM agent.
{
"provisioners": [
{
"type": "shell",
"inline": [
"if [ -f /etc/system-release ]; then",
" # Amazon Linux",
" sudo yum install -y amazon-ssm-agent",
" sudo systemctl enable amazon-ssm-agent",
" sudo systemctl start amazon-ssm-agent",
"elif [ -f /etc/lsb-release ]; then",
" # Ubuntu",
" sudo snap install amazon-ssm-agent —classic",
" sudo systemctl enable snap.amazon-ssm-agent.amazon-ssm-agent.service",
" sudo systemctl start snap.amazon-ssm-agent.amazon-ssm-agent.service",
"fi"
]
}
]
}
Alternatively, provide the path to the script which contains Agent installation shell commands.
{
"provisioners": [{
"type": "shell",
"script": "scripts/install_ssm.sh"
}]
}
When using Packer with script provisioner, the install_ssm.sh should be stored relative to your Packer configuration file (.json or .pkr .hcl).
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- CloudFormation
- Terraform
If you use CloudFormation to launch instances using AMIs that do not have SSM agent pre-installed, you can leverage the UserData property to install SSM agent.
# EC2 Instance
EC2Instance:
Type: AWS::EC2::Instance
Properties:
ImageId: !FindInMap
- RegionMap
- !Ref AWS::Region
- !Ref OperatingSystem
InstanceType: !FindInMap
- EnvironmentSettings
- !Ref EnvironmentType
- InstanceType
IamInstanceProfile: !Ref SSMInstanceProfile
UserData: !If
- !Base64
'Fn::Sub': |
#!/bin/bash
# Install SSM Agent based on OS
if [ -f /etc/os-release ]; then
. /etc/os-release
case "$ID" in
amzn|rhel)
yum install -y amazon-ssm-agent
systemctl enable amazon-ssm-agent
systemctl start amazon-ssm-agent
;;
ubuntu)
snap install amazon-ssm-agent —classic
systemctl enable snap.amazon-ssm-agent.amazon-ssm-agent.service
systemctl start snap.amazon-ssm-agent.amazon-ssm-agent.service
;;
esac
fi
When using Terraform, create a script file which contains SSM agent installation shell commands. Then use the user_data property of the instance resource to point to the installation script file.
# EC2 Instance
resource "aws_instance" "web" {
ami = data.aws_ami.amazon_linux_2.id
instance_type = "t2.micro"
subnet_id = data.aws_subnet.main.id
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.allow_ssm.id]
iam_instance_profile = aws_iam_instance_profile.ssm_profile.name
associate_public_ip_address = true
user_data = filebase64("${path.module}/scripts/install_ssm.sh")
tags = {
Name = "SSM-enabled-instance"
}
}
# Output
output "instance_id" {
value = aws_instance.web.id
}
EC2 Console/API/SDK
When launching the EC2 instance using EC2 console or any SDK, add user data with SSM Agent installation commands to an Amazon EC2 instance before you launch the instance.
- Refer to steps mentioned in this article for Linux: How do I install SSM Agent on an Amazon EC2 Linux instance at launch?
- Refer to steps mentioned in this article for Windows: How do I install AWS Systems Manager Agent (SSM Agent) on an Amazon EC2 Windows instance at launch?
Application Migration Service (MGN)
If your servers are migrated and launched using Application Migration Service, use the post-launch settings to install SSM Agent. Refer to the steps outlined here.
Amazon EKS
The latest Amazon EKS optimized AMIs install SSM Agent automatically. If you are using a customized AMI, to install SSM Agent, use preBootstrapCommands property as outlined here.
Installing SSM Agent on running instances
For instances that are already running in your environment, you can install SSM Agent using various remote access and automation methods. The installation process varies depending on your operating system type, access methods available, and network configuration. This section describes different approaches you can use to install SSM Agent on your existing instances.
Custom solution
Refer to the public blog on Automate installing AWS Systems Manager agent on unmanaged Amazon EC2 nodes. This solution uses userdata to install ssm agent and automation runbooks orchestrate this process accross regions and accounts.
Configuration management tools
If your organization uses configuration management tools such as Puppet, Chef, or Ansible, you can leverage these existing tools to deploy SSM Agent across your instances.
- Ansible
- Chef
- Puppet
- name: Install SSM Agent across fleet
hosts: all
become: yes
tasks:
- name: Detect OS family
ansible.builtin.set_fact:
os_family: "{{ ansible_facts['os_family'] }}"
- name: Install SSM Agent on RedHat family
block:
- name: Download SSM Agent RPM
get_url:
url: "https://s3.{{ aws_region }}.amazonaws.com/amazon-ssm-{{ aws_region }}/latest/linux_amd64/amazon-ssm-agent.rpm"
dest: /tmp/amazon-ssm-agent.rpm
mode: '0644'
- name: Install SSM Agent
yum:
name: /tmp/amazon-ssm-agent.rpm
state: present
when: os_family == "RedHat"
- name: Install SSM Agent on Debian family
block:
- name: Install SSM Agent via Snap
community.general.snap:
name: amazon-ssm-agent
classic: yes
when: os_family == "Debian"
- name: Enable and start SSM Agent
systemd:
name: amazon-ssm-agent
enabled: yes
state: started
- name: Verify installation
command: systemctl status amazon-ssm-agent
register: ssm_status
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Report status
debug:
var: ssm_status.stdout_lines
if $facts['os']['family'] == 'RedHat' {
package { 'amazon-ssm-agent':
ensure => installed,
source => 's3.amazonaws.com/ec2-downloads-windows/SSMAgent/latest/linux_amd64/amazon-ssm-agent.rpm',
provider => 'rpm',
}
} elsif $facts['os']['family'] == 'Debian' {
package { 'amazon-ssm-agent':
ensure => installed,
source => 's3.amazonaws.com/ec2-downloads-windows/SSMAgent/latest/debian_amd64/amazon-ssm-agent.deb',
provider => 'dpkg',
}
}
service { 'amazon-ssm-agent':
ensure => running,
enable => true,
require => Package['amazon-ssm-agent'],
}
# cookbooks/ssm_agent/recipes/default.rb
case node['platform_family']
when 'rhel'
remote_file '/tmp/amazon-ssm-agent.rpm' do
source "https://s3.#{node['region']}.amazonaws.com/amazon-ssm-#{node['region']}/latest/linux_amd64/amazon-ssm-agent.rpm"
mode '0644'
action :create
end
package 'amazon-ssm-agent' do
source '/tmp/amazon-ssm-agent.rpm'
action :install
end
when 'debian'
execute 'install_ssm_agent' do
command 'snap install amazon-ssm-agent —classic’
not_if 'snap list | grep amazon-ssm-agent'
end
end
service 'amazon-ssm-agent' do
action [:enable, :start]
end
EC2 user data
By default, user data command and cloud-init directives run only during the first boot cycle when an EC2 instance is launched. However, you can configure your user data command and cloud-init directives with a mime multi-part file.
To update the user data, stop the Instance. Click on Actions, Select Instance settings and choose Edit User Data.
- Linux
- Windows
Content-Type: multipart/mixed; boundary="//"
MIME-Version: 1.0
--//
Content-Type: text/cloud-config; charset="us-ascii"
MIME-Version: 1.0
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 7bit
Content-Disposition: attachment;
filename="cloud-config.txt"
#cloud-config
cloud_final_modules:
- [scripts-user, always]
--//
Content-Type: text/x-shellscript; charset="us-ascii"
MIME-Version: 1.0
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 7bit
Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="userdata.txt"
#!/bin/bash
# Amazon Linux 2, RHEL
dnf install -y s3.amazonaws.com/ec2-downloads-windows/SSMAgent/latest/linux_amd64/amazon-ssm-agent.rpm
systemctl enable amazon-ssm-agent
systemctl start amazon-ssm-agent
--//--
Note: The below PowerShell script works only with the EC2Launch v2 launch agent.
<powershell>
$dir = $env:TEMP + "\ssm"
New-Item -ItemType directory -Path $dir -Force
cd $dir
(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("https://s3.amazonaws.com/ec2-downloads-windows/SSMAgent/latest/windows_amd64/AmazonSSMAgentSetup.exe", $dir + "\AmazonSSMAgentSetup.exe")
Start-Process .\AmazonSSMAgentSetup.exe -ArgumentList @("/q", "/log", "install.log") -Wait
</powershell>
<persist>true</persist>
When done programmatically using the ModifyInstanceAttribute API, this script needs to be converted to base64-encoded text.
Group Policy (for Windows)
While Group Policy traditionally supports .msi packages, the AWS Systems Manager (SSM) Agent comes as an .exe file. To overcome this limitation, we'll use a combination of Group Policy and Scheduled Tasks to deploy the SSM Agent across your Windows environment.
-
Create (or modify an existing) GPO in the appropriate hierarchy/OU in Active Directory. Edit the policy to utilize the computer scheduled task script configuration.
-
The option is located under Computer Configuration | Preferences | Control Panel Settings | Scheduled Tasks | Right-click and select New→Immediate Task
-
Select Create for the action, give the task a name, and specify
NT AUTHORITY\Systemas the user account to run the task. Click on the radio button for Run whether user is logged on or not and click the Triggers tab to proceed to the next section.
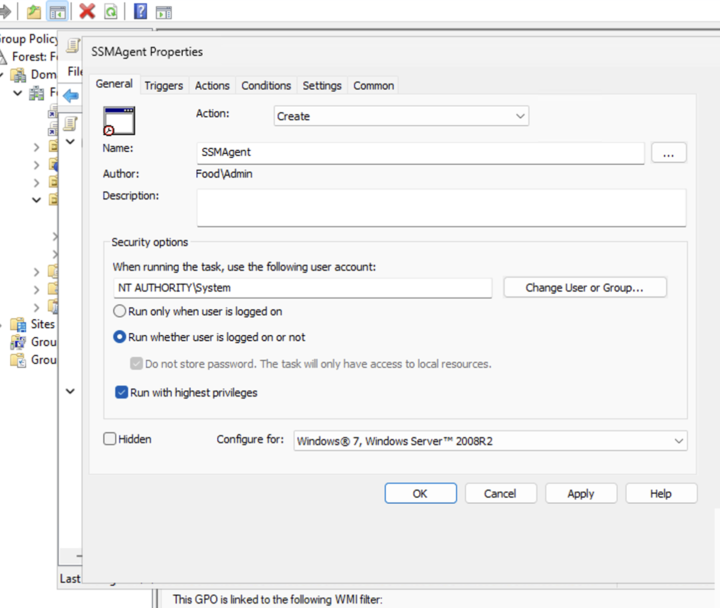
-
For triggers, choose one time.
-
Create a new action to Start a program and choose
powershell.exeand for the Argument use the following:
-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "$dir = $env:TEMP + '\ssm'; New-Item -ItemType directory -Path $dir -Force; Set-Location $dir; (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('https://s3.amazonaws.com/ec2-downloads-windows/SSMAgent/latest/windows_amd64/AmazonSSMAgentSetup.exe', $dir + '\AmazonSSMAgentSetup.exe'); Start-Process .\AmazonSSMAgentSetup.exe -ArgumentList @('/q', '/log', 'install.log') -Wait"
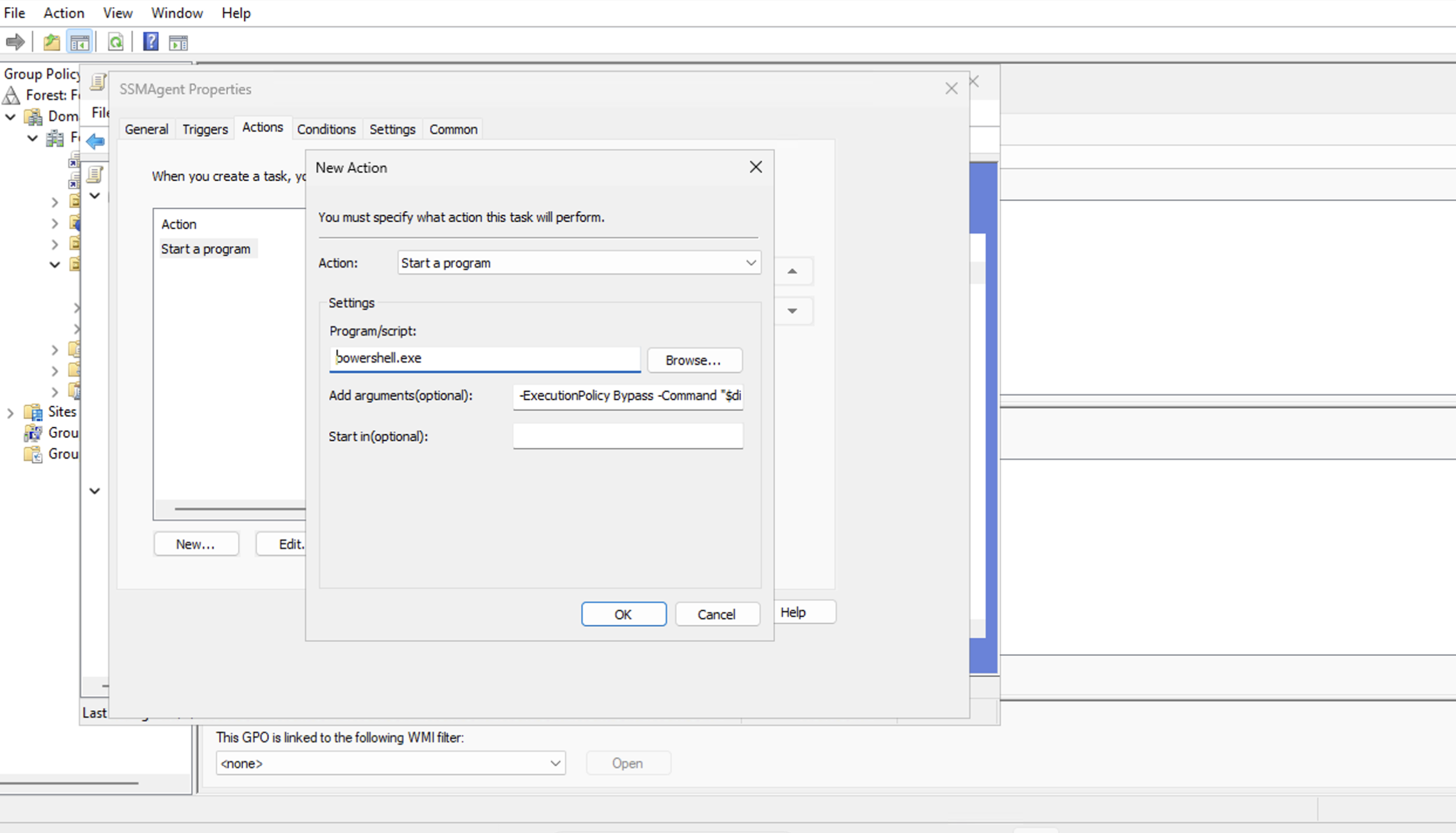
-
Click OK on New Action window and click OK on Properties window to close out those dialogues.
-
Once this is complete, any linked computers should get the installer pushed to them when the GP policy updates or when using
gpudate /forcefrom the command prompt to force that action.
For more information, see Automate Registering Windows Managed Nodes in AWS Systems Manager.
SSH (for Linux)
For Linux instances accessible via SSH, you can automate the SSM Agent installation using the following sample script. This script detects the OS type and installs the appropriate package.
#!/bin/bash
USERNAME=ec2-user
HOSTS=("192.168.1.121" "192.168.1.122" "192.168.1.123")
KEY_PATH="/path/to/your/key.pem"
for HOSTNAME in ${HOSTS}; do
# Detect OS type
OS_TYPE=$(ssh -i "${KEY_PATH}" -l ${USERNAME} ${HOSTNAME} "cat /etc/os-release | grep '^ID=' | cut -d= -f2 | tr -d '\"'")
case ${OS_TYPE} in
"amzn"|"rhel"|"centos")
SCRIPT="sudo yum install -y s3.amazonaws.com/ec2-downloads-windows/SSMAgent/latest/linux_amd64/amazon-ssm-agent.rpm && sudo systemctl start amazon-ssm-agent"
;;
"ubuntu"|"debian")
SCRIPT="wget s3.amazonaws.com/ec2-downloads-windows/SSMAgent/latest/debian_amd64/amazon-ssm-agent.deb && sudo dpkg -i amazon-ssm-agent.deb && sudo systemctl start amazon-ssm-agent"
;;
*)
echo "Unsupported OS on ${HOSTNAME}"
continue
;;
esac
ssh -i "${KEY_PATH}" -l ${USERNAME} ${HOSTNAME} "${SCRIPT}"
done
Amazon EKS - Existing instances
The latest Amazon EKS optimized AMIs install SSM Agent automatically. If you are using a customized AMI, to install SSM Agent on running worker nodes, use Kubernetes Daemonset as outlined here.
Amazon Workspaces
Use the customized solution documented here.
Managing IAM permissions for SSM Agent
Proper IAM permissions are crucial for SSM Agent functionality. AWS provides multiple approaches to manage these permissions, from manual instance profile attachment to automated organization-wide solutions.
Default Host Management Configuration (DHMC)
DHMC is AWS's recommended approach for managing SSM Agent permissions across your organization. It makes it possible to manage EC2 instances without your having to manually create an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) instance profile. Instead, Default Host Management Configuration creates and applies a default IAM role to ensure that Systems Manager has permissions to manage all instances in the AWS account and AWS Region where it's activated.
Methods to enable DHMC:
- Through Unified Console Experience: When onboarding to unified console experience, DHMC is automatically enabled. This is enabled using a State Manager association created during onboarding and will enable DHMC in each target account and region.
- Using Fleet Manager: You can turn on the Default Host Management Configuration from the Fleet Manager console. You must turn on the Default Host Management Configuration one by one in each Region you where you want your Amazon EC2 instances managed. Refer to the steps here.
- Through CLI/SDK: This is done by creating the required role and updating the service setting using AWS CLI/SDK. You must turn on the Default Host Management Configuration one by one in each Region you where you want your Amazon EC2 instances managed. Refer to steps here.
- Though Quick Setup: With Quick Setup, you can activate Default Host Management Configuration for all accounts and Regions that have been added to your organization in AWS Organizations. Refer to steps here.
- Using CloudFormation: You can also use CloudFormation, to enable DHMC is multi accounts and region using StackSets. Refer to this blog.
Individual instance permissions
If you are not using DHMC, the permission for SSM agent must be granted at each instance level by using IAM Instance Profiles. We recommend creating the Instance Profile with the recommended Amazon Managed Policy for SSM agent, AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore. Additional permissions to this instance profile will be required depending on the use case. See Additional policy considerations for managed instances in User guide which discusses creating an IAM instance profile for SSM agent use and additional policy considerations.
Attaching instance profile to EC2 instances at launch
- CloudFormation
- Terraform
If you are using CloudFormation to launch Instances, you can create an IAM instance profile resource and refer to it in your instance resource.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Resources:
SSMInstanceRole:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::Role'
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: '2012-10-17'
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service: ec2.amazonaws.com
Action: sts:AssumeRole
ManagedPolicyArns:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore
SSMInstanceProfile:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::InstanceProfile'
Properties:
Path: /
Roles:
- !Ref SSMInstanceRole
EC2Instance:
Type: 'AWS::EC2::Instance'
Properties:
IamInstanceProfile: !Ref SSMInstanceProfile
# Other instance properties
When deploying Autoscaling groups, the Launch template resource property can refer to use the Instance Profile.
# ASG with SSM Instance Profile
Resources:
AutoScalingGroup:
Type: AWS::AutoScaling::AutoScalingGroup
Properties:
LaunchTemplate:
LaunchTemplateId: !Ref LaunchTemplate
Version: !GetAtt LaunchTemplate.LatestVersionNumber
LaunchTemplate:
Type: AWS::EC2::LaunchTemplate
Properties:
LaunchTemplateData:
IamInstanceProfile:
Name: !Ref SSMInstanceProfile
If you are using Terraform to launch instances, you can create an IAM Instance Profile resource and refer it in your Instance resource.
# IAM Role and Instance Profile
resource "aws_iam_role" "ssm_role" {
name = "SSMManagedInstanceRole"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Action = "sts:AssumeRole"
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = {
Service = "ec2.amazonaws.com"
}
}
]
})
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "ssm_policy" {
role = aws_iam_role.ssm_role.name
policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore"
}
resource "aws_iam_instance_profile" "ssm_profile" {
name = "SSMManagedInstanceProfile"
role = aws_iam_role.ssm_role.name
}
# EC2 Instance with Profile
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
# ... other configuration ...
iam_instance_profile = aws_iam_instance_profile.ssm_profile.name
}
Launching instances using Systems Manager Automation runbooks
AWS-CreateManagedLinuxInstance and AWS-CreateManagedWindowsInstance are pre-configured Systems Manager Automation runbooks that automate the process of creating and configuring managed instances. These runbooks ensure the instance profile have the required SSM Permissions are attached to the launched instances.
Attaching instance profiles to already running EC2 instances
-
Using Quick Setup (Recommended): Using Amazon EC2 host management using Quick Setup, you can configure to add the required IAM policies to the existing instance profiles attached to your instances, or to allow Quick Setup to create the IAM policies and instance profiles with the permissions needed for the configuration you choose. This option can target instances in multiple accounts in organization or specific OUs.
-
Using Systems Manager Automation : You can use the automation runbook AWS-SetupManagedRoleOnEc2Instance to configure an instance with the SSMRoleForManagedInstance managed IAM role for Systems Manager access.. If the specified role does not exist, it will be created by the automation. To target instances in multiple account and regions, run the automation in multi-account/multi-Region mode.