Sample AWS Blockchain Node Runner app for Tezos Nodes
| Contributed by |
|---|
| @AhGhanima, @chrisdotn |
Architecture Overview
This blueprint has two options for running nodes. You can set up a single JSON RPC node or multiple nodes in highly-available setup. The details are below.
Single RPC node setup
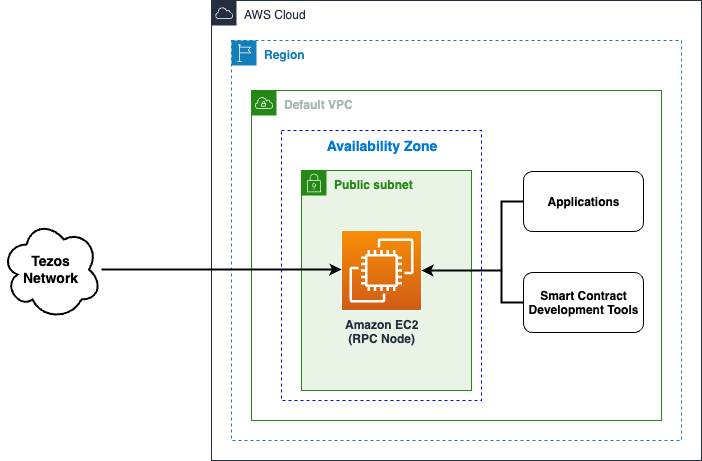
This setup is for small scale PoC or development environments. It deploys a single EC2 instance with the tezos client. The RPC port is exposed only to internal IP range of the VPC, while P2P ports allow external access to keep the client synced.
Highly available setup
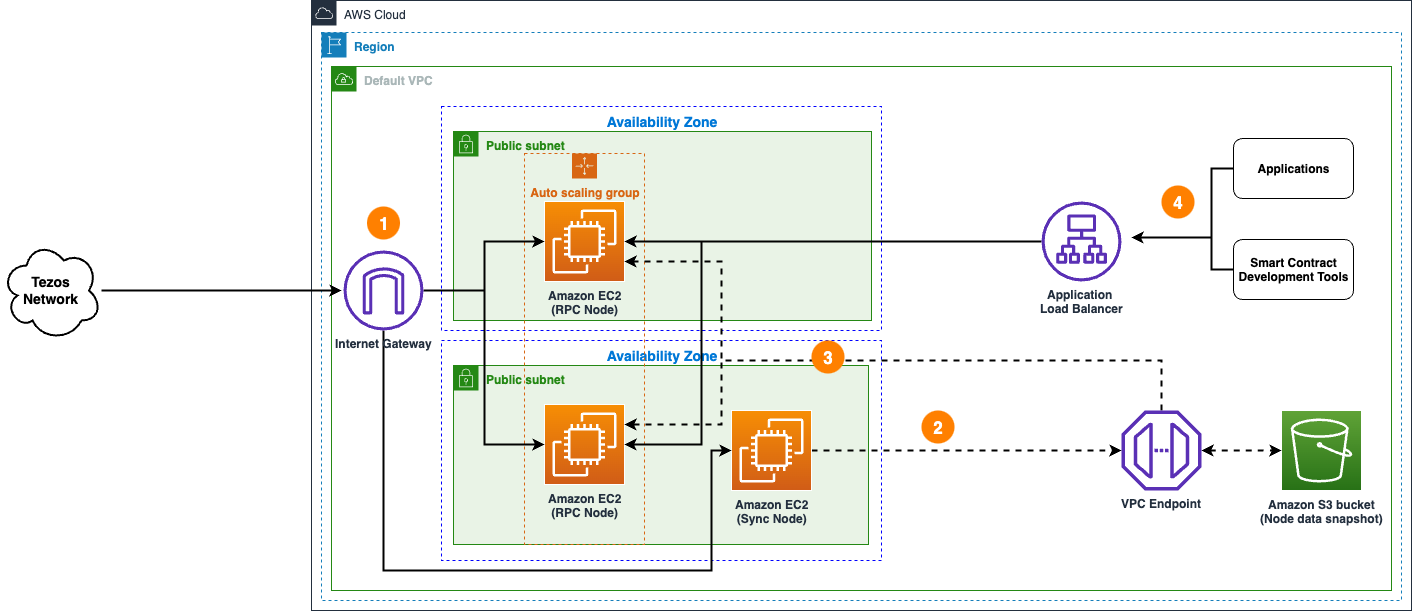
- An ongoing data synchronization process is configured with nodes in the Tezos network with a sync node and RPC nodes.
- The sync node is used to create a copy of node's state data in Amazon S3 bucket.
- When new RPC nodes are provisioned, they copy state data from Amazon S3 bucket to speed up the initial sync process.
- Applications and smart contract development tools access highly available RPC nodes behind the Application Load Balancer.
Solution Walkthrough
Open AWS CloudShell
To begin, ensure you login to your AWS account with permissions to create and modify resources in IAM, EC2, EBS, VPC, S3, KMS, and Secrets Manager.
From the AWS Management Console, open the AWS CloudShell, a web-based shell environment. If unfamiliar, review the 2-minute YouTube video for an overview and check out CloudShell with VPC environment that we'll use to test nodes API from internal IP address space.
Once ready, you can run the commands to deploy and test blueprints in the CloudShell.
Clone this repository and install dependencies
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/aws-blockchain-node-runners.git
cd aws-blockchain-node-runners
npm install
NOTE: In this tutorial we will set all major configuration through environment variables, but you also can modify parameters in config/config.ts.
Prepare to deploy nodes
-
Make sure you are in the root directory of the cloned repository
-
If you have deleted or don't have the default VPC, create default VPC
aws ec2 create-default-vpc
NOTE: You may see the following error if the default VPC already exists:
An error occurred (DefaultVpcAlreadyExists) when calling the CreateDefaultVpc operation: A Default VPC already exists for this account in this region.. That means you can just continue with the following steps.
NOTE: The default VPC must have at least two public subnets in different Availability Zones, and public subnet must set
Auto-assign public IPv4 addresstoYES.
- Configure your setup
Create your own copy of .env file and edit it:
# Make sure you are in aws-blockchain-node-runners/lib/tezos
cd lib/tezos
pwd
cp ./sample-configs/.env-sample-full .env
nano .env
NOTE: You can find more examples inside the
sample-configsdirectory.
- Deploy common components such as IAM role, and Amazon S3 bucket to store data snapshots
pwd
# Make sure you are in aws-blockchain-node-runners/lib/tezos
npx cdk deploy tz-common
Option 1: Single RPC Node
- Deploy Single RPC Node
pwd
# Make sure you are in aws-blockchain-node-runners/lib/tezos
npx cdk deploy tz-single-node --json --outputs-file single-node-deploy.json
NOTE: The default VPC must have at least two public subnets in different Availability Zones, and public subnet must set
Auto-assign public IPv4 addresstoYES.
The EC2 instance will deploy, initialize the node and start the first sync. In Cloudformation the instance will show as successful once the node is running. From that point it still takes a while until the node is synced to the blockchain. You can check the sync status with the REST call below in step 4. If the `curl cannot connect to the node on port 8732, then the node is still importing. Once that's done, the curl command works.
-
After starting the node you need to wait for the inital syncronization process to finish. It may take from an hour to half a day depending on the the state of the network. You can use Amazon CloudWatch to track the progress. To see them:
- Navigate to CloudWatch service (make sure you are in the region you have specified for
AWS_REGION) - Open
Dashboardsand selecttz-single-node-<type>-<network>from the list of dashboards.
- Navigate to CloudWatch service (make sure you are in the region you have specified for
-
Once the initial synchronization is done, you should be able to access the RPC API of that node from within the same VPC. The RPC port is not exposed to the Internet. Run the following query against the private IP of the single RPC node you deployed:
INSTANCE_ID=$(cat single-node-deploy.json | jq -r '..|.singleinstanceid? | select(. != null)')
NODE_INTERNAL_IP=$(aws ec2 describe-instances --instance-ids $INSTANCE_ID --query 'Reservations[*].Instances[*].PrivateIpAddress' --output text)
echo "NODE_INTERNAL_IP=$NODE_INTERNAL_IP"
Copy output from the last echo command with NODE_INTERNAL_IP=<internal_IP> and open CloudShell tab with VPC environment to access internal IP address space. Paste NODE_INTERNAL_IP=<internal_IP> into the new CloudShell tab. Then query the API:
# IMPORTANT: Run from CloudShell VPC environment tab
# We query if the node is synced to main
curl http://$NODE_INTERNAL_IP:8732/chains/main/is_bootstrapped
The result should be like this (the actual balance might change):
{"bootstrapped":true,"sync_state":"synced"}
Option 2: Highly Available RPC Nodes
- Deploy Snapshot Node
pwd
# Make sure you are in aws-blockchain-node-runners/lib/tezos
npx cdk deploy tz-snapshot-node --json --outputs-file sync-node-deploy.json
NOTE: The default VPC must have at least two public subnets in different Availability Zones, and public subnet must set
Auto-assign public IPv4 addresstoYES.
-
After starting the node you need to wait for the inital syncronization process to finish. It may take from an hour to half a day depending the state of the network. You can use Amazon CloudWatch to track the progress. To see them:
- Navigate to CloudWatch service (make sure you are in the region you have specified for
AWS_REGION) - Open
Dashboardsand selecttz-snapshot-node-<type>-<network>from the list of dashboards.
- Navigate to CloudWatch service (make sure you are in the region you have specified for
Once synchronization process is over, the script will automatically stop the client and copy all the contents of the /data directory to your snapshot S3 bucket. That may take from 30 minutes to about 2 hours. During the process on the dashboard you will see lower CPU and RAM utilization but high data disc throughput and outbound network traffic. The script will automatically start the clients after the process is done.
NOTE: The snapshot backup process will automatically run ever day at midnight time of the time zone were the sync node runs. To change the schedule, modify
crontabof the root user on the node's EC2 instance.
- Configure and deploy 2 RPC Nodes
pwd
# Make sure you are in aws-blockchain-node-runners/lib/tezos
npx cdk deploy tz-ha-nodes --json --outputs-file rpc-node-deploy.json
- Give the new RPC nodes about an hour to initialize and then run the following query against the load balancer behind the RPC node created
export RPC_ABL_URL=$(cat rpc-node-deploy.json | jq -r '..|.alburl? | select(. != null)')
echo RPC_ALB_URL=$RPC_ALB_URL
# IMPORTANT: Run from CloudShell VPC environment tab
curl http://$RPC_ABL_URL:8732/chains/main/is_bootstrapped
The result should be like this:
{"bootstrapped":true,"sync_state":"synced"}
If the nodes are still starting and catching up with the chain, you will see the following repsonse:
<html>
<head><title>503 Service Temporarily Unavailable</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>503 Service Temporarily Unavailable</h1></center>
</body>
NOTE: By default and for security reasons the load balancer is available only from within the default VPC in the region where it is deployed. It is not available from the Internet and is not open for external connections. Before opening it up please make sure you protect your RPC APIs.
Clearing up and undeploying everything
Destroy RPC Nodes, HA Nodes and Common components
# Setting the AWS account id and region in case local .env file is lost
export AWS_ACCOUNT_ID=<your_target_AWS_account_id>
export AWS_REGION=<your_target_AWS_region>
pwd
# Make sure you are in aws-blockchain-node-runners/lib/tezos
# Destroy Single RPC Node
cdk destroy tz-single-node
# Destroy RPC Nodes
cdk destroy tz-ha-nodes
# Destroy Sync Node
cdk destroy tz-snapshot-node
# You need to manually delete an s3 bucket with a name similar to 'tz-snapshots-$accountid-tz-nodes-common' on the console,firstly empty the bucket,secondly delete the bucket,and then execute
# Delete all common components like IAM role and Security Group
cdk destroy tz-common
FAQ
- How to check the logs from the EC2 user-data script?
Note: In this tutorial we chose not to use SSH and use Session Manager instead. That allows you to log all sessions in AWS CloudTrail to see who logged into the server and when. If you receive an error similar to
SessionManagerPlugin is not found, install Session Manager plugin for AWS CLI
pwd
# Make sure you are in aws-blockchain-node-runners/lib/tezos
export INSTANCE_ID=$(cat single-node-deploy.json | jq -r '..|.single-node-instance-id? | select(. != null)')
echo "INSTANCE_ID=" $INSTANCE_ID
aws ssm start-session --target $INSTANCE_ID --region $AWS_REGION
sudo cat /var/log/cloud-init-output.log
- How can check the status of the node service?
export INSTANCE_ID=$(cat single-node-deploy.json | jq -r '..|.node-instance-id? | select(. != null)')
echo "INSTANCE_ID=" $INSTANCE_ID
aws ssm start-session --target $INSTANCE_ID --region $AWS_REGION
sudo systemctl status node
- How to check the logs of the clients running on my node?
pwd
# Make sure you are in aws-blockchain-node-runners/lib/solana
export INSTANCE_ID=$(cat single-node-deploy.json | jq -r '..|.node-instance-id? | select(. != null)')
echo "INSTANCE_ID=" $INSTANCE_ID
aws ssm start-session --target $INSTANCE_ID --region $AWS_REGION
sudo su bcuser
sudo journalctl -o cat -fu node
- How to check the logs of data backup service on sync node?
pwd
# Make sure you are in aws-blockchain-node-runners/lib/solana
export INSTANCE_ID=$(cat sync-node-deploy.json | jq -r '..|.node-instance-id? | select(. != null)')
echo "INSTANCE_ID=" $INSTANCE_ID
aws ssm start-session --target $INSTANCE_ID --region $AWS_REGION
sudo su bcuser
sudo journalctl -o cat -fu s3-sync